When it comes to marketing, the ultimate goal is to drive results - increased sales, leads, or revenue. But how can you know for sure that your marketing efforts are truly driving those results? This is where the concept of incrementality comes in.
Incrementality is the additional impact or benefit that a marketing campaign or activity has on a specific outcome beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign. Essentially, it's the "extra boost" that your marketing provides.
Let's imagine you're running a digital ad campaign to promote a new product. You might think that your campaign is responsible for all the sales of that product during the campaign period, but that's not necessarily true. Some of those sales may have happened even without the campaign - perhaps due to organic search or other factors. Incrementality testing allows you to isolate the impact of the campaign and determine how many of those sales were truly driven by the campaign.
By measuring incrementality, you can gain a more accurate understanding of the true impact of your marketing efforts. This is important because it allows you to optimize your marketing spending and ensure that you are achieving the highest possible return on your investment. If your campaign is driving incremental value - that is, if it's generating additional sales that wouldn't have happened without the campaign - then you can feel confident that you're investing your marketing dollars wisely.
What is Incrementality Testing?
Incrementality testing is a statistical method used in marketing to determine the incremental impact of a specific campaign or activity on a desired outcome. Incrementality testing is designed to isolate the impact of a campaign and determine whether it had an incremental effect beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign.
To conduct an incrementality test, businesses typically divide their audience into two groups - the test group, which is exposed to the campaign or activity, and the control group, which is not. By comparing the behavior of the test group to the control group, businesses can determine the incremental impact of the campaign or activity.
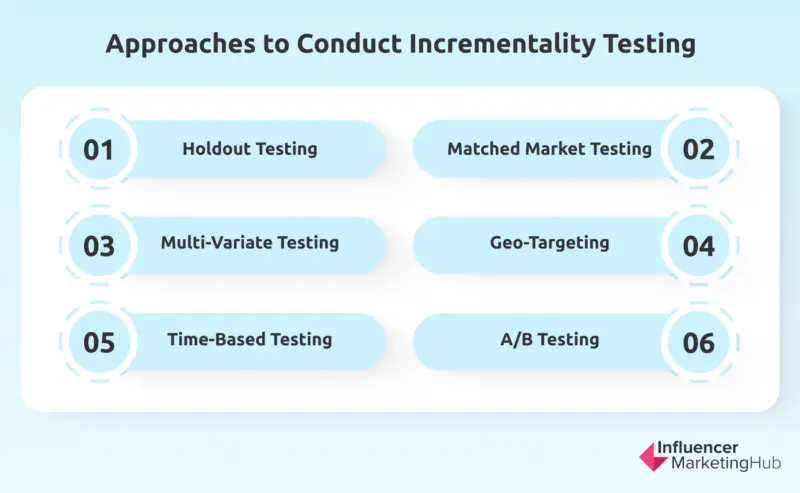
There are various approaches to conducting incrementality testing, including:
- Holdout Testing: This approach involves randomly selecting a portion of the audience and not exposing them to the campaign, while the remaining audience is exposed. The behavior of the two groups is then compared to determine the incremental impact of the campaign.
- Matched Market Testing: This involves selecting a similar market where the campaign is not run and comparing the outcomes to the test market where the campaign is run. This approach is particularly useful for businesses operating in multiple markets, as it provides a way to measure the impact of the campaign across different markets.
- Multi-Variate Testing: This involves testing multiple variables at the same time to determine which combination of variables has the highest incremental impact.
- Geo-Targeting: This involves targeting specific geographic areas with the campaign and comparing the behavior of those areas to non-targeted areas to determine the incremental impact of the campaign.
- Time-Based Testing: This involves running the campaign during different times of the day, week, or month to determine the incremental impact of the campaign during different periods.
- A/B Testing: Another popular approach to incrementality testing. In A/B testing, the audience is randomly assigned to two groups - the test group, which is exposed to the campaign or activity, and the control group, which is not. The behavior of the two groups is then compared to determine the incremental impact of the campaign.
By isolating the impact of a campaign and determining whether it had an incremental effect beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign, businesses can optimize their marketing strategies and achieve better results. With different approaches to conducting incrementality testing, businesses can choose the method that best suits their needs and achieve the most accurate results.
How to Measure Incrementality
Incrementality can be calculated using the formula:
This metric provides a clear indication of the incremental impact of the campaign and can be used to compare the effectiveness of different campaigns.
When it comes to measuring the incremental impact of a marketing campaign or activity, businesses have several metrics at their disposal. These metrics are designed to provide insights into the effectiveness of the campaign and its impact on the desired outcome.
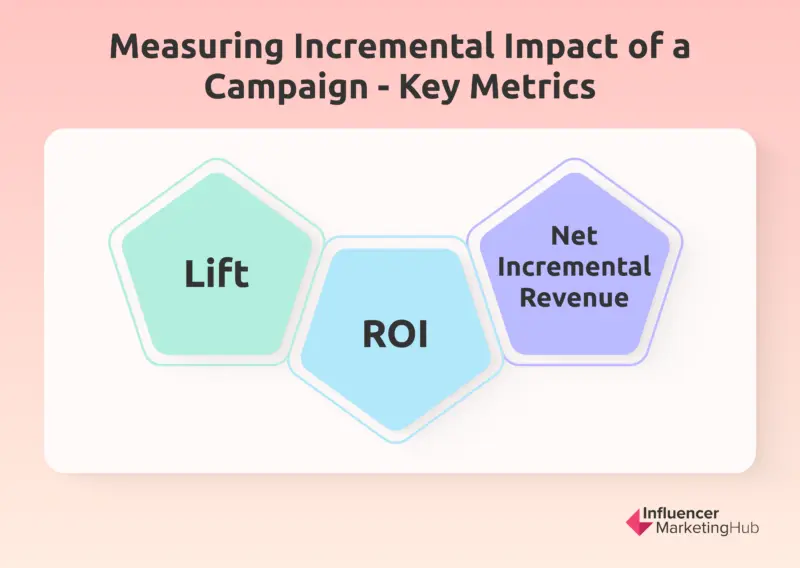
To measure the incremental impact of a campaign or activity, several metrics can be used, including:
- Lift: This is one of the most commonly used metrics, and it’s the percentage change in the desired outcome (e.g., sales, leads, revenue) between the test and control groups. This metric provides a clear indication of the incremental impact of the campaign and can be used to compare the effectiveness of different campaigns.
- ROI: Another important metric, is the return on investment from the campaign, taking into account the cost of the campaign and the incremental impact on the desired outcome. This metric is particularly useful for businesses looking to optimize their marketing spending and ensure that they are achieving the highest possible return on their investment.
- Net Incremental Revenue (NIR): NIR is another metric that businesses can use to measure the incremental impact of their campaigns. This metric calculates the additional revenue generated by the campaign after deducting the cost of the campaign. NIR is particularly useful for businesses looking to understand the financial impact of their campaigns and optimize their marketing spending accordingly.
To measure the incremental impact of a campaign, businesses can use different methods, including statistical analysis, time series decomposition, and machine learning algorithms. These methods are designed to provide accurate and reliable insights into the effectiveness of the campaign and its impact on the desired outcome.
In addition, there are various tools and software available, such as Google Ads and Facebook Ads, which provide incrementality testing capabilities. These tools allow businesses to easily conduct incrementality testing and gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns.
How Does Incrementality Testing Actually Work
Incrementality testing is a sophisticated technique that can help businesses measure the true impact of their marketing campaigns. But how does it actually work? As we mentioned above, incrementality testing involves comparing the behavior of a test group (those who were exposed to the campaign) with a control group (those who were not).
By isolating the impact of the campaign and comparing the behavior of the two groups, businesses can determine whether the campaign had an incremental impact on the desired outcome beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign.
For example, a study conducted by Facebook found that incrementality testing can help businesses improve their ROI by an average of 71%. In the study, Facebook worked with a retail advertiser to conduct an incrementality test on Facebook Ads campaign. By comparing the behavior of the test and control groups, the retailer was able to determine that the campaign had a direct incremental effect of 34% on its sales. Based on this insight, the retailer was able to optimize its campaign and achieve a 71% increase in ROI.
Importance of Defining Goals in Incrementality Testing
One of the most important aspects of conducting an effective incrementality test is to clearly define your goals and desired outcomes. Before running a test, it's important to have a specific objective in mind - whether that's to increase sales, leads, or revenue. By defining your goals up front, you can ensure that your test is focused on measuring the impact of your marketing campaigns on those specific outcomes.
For example, let's say you're running a digital ad campaign to promote a new product. Your goal might be to increase sales of that product during the campaign period. By defining this objective up front, you can design your incrementality test to measure the incremental impact of the campaign on sales specifically. This can help you gain a more accurate understanding of the true impact of the campaign and make informed decisions about how to optimize your spending for maximum return on investment.
In addition to defining your goals, it's also important to establish a clear hypothesis for your incrementality test. This can help guide your test design and ensure that you are measuring the right outcomes. By defining your hypothesis up front, you can ensure that your test is focused on answering a specific question and providing meaningful insights into the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
Ultimately, defining your goals and hypotheses upfront can help you conduct more effective incrementality tests and make data-driven decisions to achieve the greatest possible return on investment.
Audience Segmentation In Incrementality Testing
Audience segmentation is another important factor to consider when conducting an incrementality test. By segmenting your audience into different groups, you can gain more granular insights into the impact of your marketing campaigns on specific segments of your customer base. This can be particularly useful for businesses with diverse customer segments, as it can help identify which segments are most responsive to different types of marketing campaigns.
For example, let's say you're running an email marketing campaign to promote a new product. By segmenting your email list into different groups based on factors like demographics or purchase history, you can conduct separate incrementality tests for each group and gain more targeted insights into the effectiveness of your campaign. This can help you optimize your spending and targeting for each segment of your audience and achieve the greatest possible return on investment.
In addition to segmenting your audience for incrementality testing, it's also important to consider other factors like timing and frequency of your campaigns. By conducting tests at different times or frequencies, you can gain insights into how these factors impact the incremental impact of your campaigns on desired outcomes. Ultimately, audience segmentation is a key component of effective incrementality testing, and can help businesses gain more nuanced insights into the impact of their marketing campaigns on specific customer segments.
Incrementality Testing vs. AB Testing
Incrementality testing is often compared to AB testing, which is another commonly used technique in marketing. While both methods do involve testing the impact of a campaign or activity, there are some key differences.
AB testing involves randomly dividing the audience into two groups and exposing one group to a variant of the campaign, while the other group sees the original version. The behavior of the two groups is then compared to determine which version of the campaign is more effective. AB testing is a valuable tool for optimizing the performance of a campaign by testing different variations to determine which version achieves the best results.
In contrast, incrementality testing focuses on determining the incremental impact of a campaign on a particular outcome. It involves randomly assigning the audience to two groups, one exposed to the campaign (the test group) and the other not exposed (the control group). The behavior of the two groups is then compared to determine the incremental impact of the campaign. Incrementality testing is designed to isolate the impact of the campaign and determine whether it had an incremental effect beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign.
The key difference between AB testing and incrementality testing is that AB testing compares different versions of a campaign, while incrementality testing focuses on measuring the incremental impact of a campaign on a specific outcome. AB testing is useful for optimizing the performance of a campaign, while incrementality testing is useful for determining the effectiveness of the campaign itself and its impact on the desired outcome.
Conclusion
Unlocking the true impact of marketing campaigns is essential to drive growth and success in today's competitive market. Incrementality testing is a powerful technique that helps businesses measure the incremental impact of a campaign on specific outcomes beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign.
By measuring incremental impact, businesses can make informed decisions about their marketing strategies, optimize their spending, and achieve the highest possible return on investment. The importance of defining goals and hypotheses up front, audience segmentation, and selecting the right metrics and testing methods are key components of conducting effective incrementality tests.
Moreover, by understanding the differences between AB testing and incrementality testing, businesses can choose the approach that best suits their needs and achieve the most accurate results. Ultimately, businesses that invest in incrementality testing can see significant improvements in their advertising effectiveness, customer acquisition efforts, and return on investment.
Therefore, it's important for businesses to embrace the power of incrementality testing to achieve growth and success in the ever-changing marketing landscape.
Incrementality testing is a statistical method used in marketing to determine the incremental impact of a specific campaign or activity on a desired outcome. It is designed to isolate the impact of a campaign and determine whether it had an incremental effect beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign. Incrementality testing allows businesses to measure the true impact of their marketing campaigns and make data-driven decisions to optimize their spending for maximum return on investment. By isolating the impact of a campaign and determining whether it had an incremental effect beyond what would have been achieved without the campaign, businesses can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their marketing strategies. Incrementality testing typically involves dividing the audience into two groups - the test group, which is exposed to the campaign or activity, and the control group, which is not. By comparing the behavior of the test group to the control group, businesses can determine the incremental impact of the campaign or activity. Common metrics used in incrementality testing include lift, ROI, and net incremental revenue (NIR). These metrics are designed to provide insights into the effectiveness of the campaign and its impact on the desired outcome. There are several approaches to conducting incrementality testing, including holdout testing, matched market testing, multi-variate testing, geo-targeting, time-based testing, and A/B testing. Each approach has its own strengths and weaknesses, and businesses should choose the approach that best suits their needs. A/B testing compares different versions of a campaign, while incrementality testing focuses on measuring the incremental impact of a campaign on a specific outcome. A/B testing is useful for optimizing the performance of a campaign, while incrementality testing is useful for determining the effectiveness of the campaign itself and its impact on the desired outcome. Businesses that invest in incrementality testing can see significant improvements in their advertising effectiveness, customer acquisition efforts, and return on investment. By gaining a more accurate understanding of the true impact of their marketing efforts, businesses can optimize their spending and achieve the highest possible return on investment. Frequently Asked Questions
What is incrementality testing?
Why is incrementality testing important?
How is incrementality testing conducted?
What metrics are used in incrementality testing?
What are some approaches to conducting incrementality testing?
How does incrementality testing differ from A/B testing?
What are some benefits of using incrementality testing?