HypeAuditor recently commissioned a report on The State of Influencer Marketing in 2019. It makes fascinating reading.
The 55-page report covers many faces of influencer marketing, but we found its sections on Instagram Performance and Benchmarks, and Instagram Marketing Fraud in 2018 particularly interesting. It is these sections that we concentrate on in this post.
HypeAuditor sourced its data from a wide variety of sources, including market research agencies, internet, and social media companies, news media, and their own internal analysis. They collected and aggregated open data from social platforms, catalogs, websites, crowdsourcing, and other sources.
Instagram Influencers' Performance, Benchmarks, and FRAUD:
Instagram Influencers’ Performance and Benchmarks
Engagement Rates
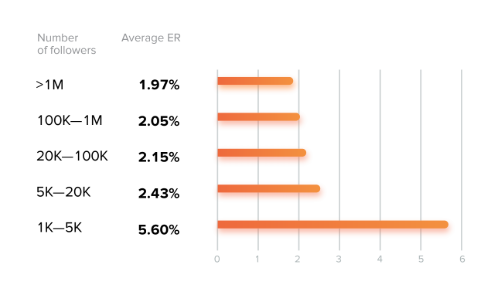
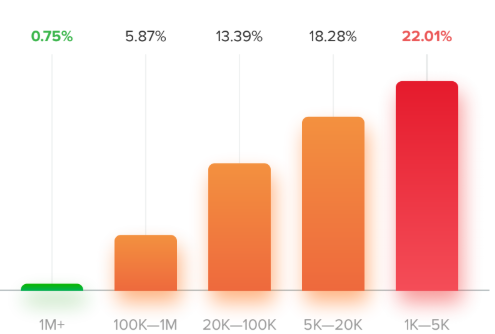
It shouldn’t surprise anyone that smaller Instrgammers can manage higher engagement rates than their larger counterparts. Nano-influencers and ordinary people have more time to engage with their limited number of followers than the mega-stars do. Also, it doesn’t take many acts of engagement to make a noticeable difference if you don’t have many followers.
It makes sense that celebrity and mega-influencers have the least engagement on their accounts. Many people follow them merely because they are famous. It doesn't mean that they necessarily take a great interest in what they have to share.
Of course, 1.97% engagement for somebody with 1 million followers implies 19,700 acts of engagement. 5.60% engagement for an account with 5,000 followers suggests an average of 280 acts of engagement. The smaller accounts may encourage comparatively more engagement, but the raw numbers for larger accounts by far outweigh engagement on everyday accounts.
HypeAuditor also compared the engagement results for this year with the 2018 results. They found that engagement has increased at all follower sizes between 2018 and 2019. For all groups of influencers (except for one follower band) the engagement rose by 22-25% over the year. The exception was for those with between 5K and 20K followers, who only increased their engagement by 6%.
Comparing Influencer Engagement and Interactions Across Countries
There are quite noticeable differences if you compare the average engagements and interactions per post across different countries.
Influencers from the United States
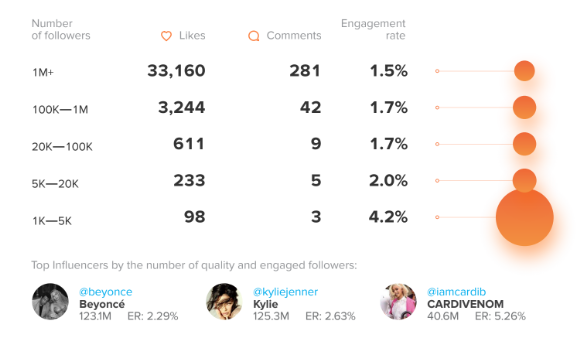
It is probably not overly surprising that the statistics relating to US influencers are relatively average compared to other countries. It can be seen that the audience of nano-influencers are more likely to like and make comments than the followers of larger influencers (although they are dwarfed in terms of raw figures, obviously). There is a definite drop in engagements per follower once influencers reach 5,000 followers.
Influencers from the United Kingdom
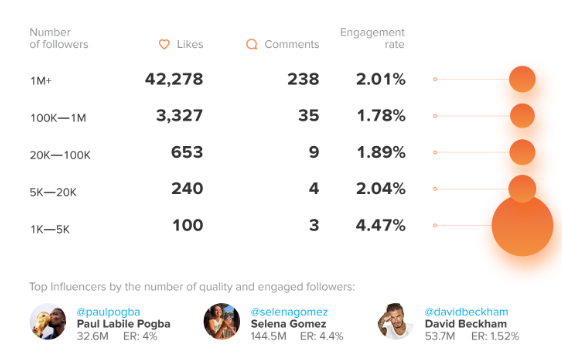
United Kingdom influencers also tend to follow a fairly typical pattern, in terms of likes and comments. Their nano-influencer audience engages almost identically to their US counterparts.
One notable difference in the UK compared to US influencers is that the engagement falls off less sharply as follower numbers rise, and actually increases (in terms of likes at least, for the celebrity mega-influencers.
Influencers from India
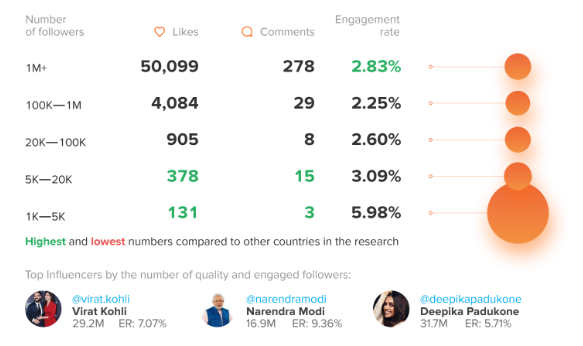
Indian influencers enjoyed some of the highest engagement in HypeAuditor’s survey. Indeed, they had the best raw Likes and Comment numbers for both nano-influencers and the smaller micro-influencers. Indian celebrities also enjoyed the best engagement rates, and these were up from the figures for influencers with between 20K and 1M followers.
HypeAuditor did observe that users from India were more likely to leave a like than a comment.
Influencers from Germany
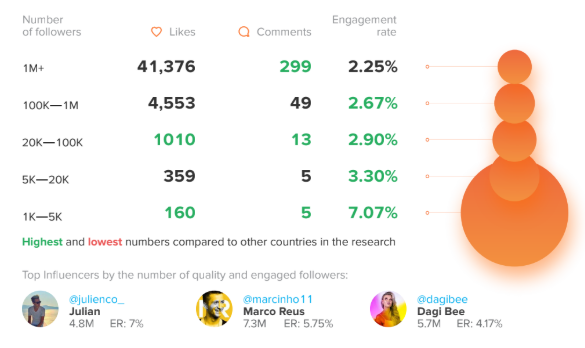
Germany was the other country to show significantly more engagement from the followers of their influencers. As you can see from the above chart, they topped the engagement rate stats for everybody except celebrities. And even celebirites’ followers liked to leave comments.
Indeed the average number of comments made by the followers of German influencers was the highest anywhere.
Influencers from Brazil
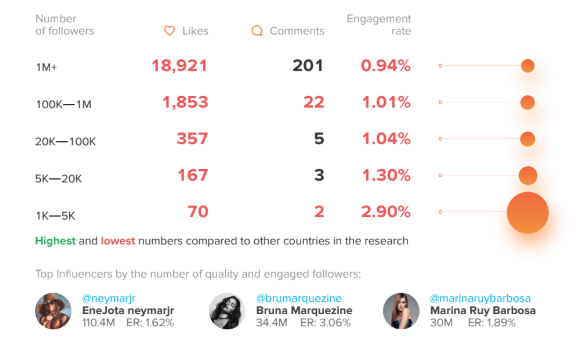
Brazillian influencers suffered from having the least active followers in the survey. Even nano-influencers had low engagement rates, and influencers with greater than 5,000 followers had exceedingly small engagement.
You have to wonder whether Brazilian influencers suffer from fake followers more than other countries, as such a low engagement rate indicates a high probability that the follower count of these influencers is inflated artificially.
Instagram Marketing Fraud
HypeAuditor devoted an entire chapter of their report to Instagram Marketing fraud in 2018. They began by setting a definition for a fraud-free influencer: "an influencer with a big percentage of real people among followers, authentic engagement and without anomalies on [their] followers and followings graphs."
How to Detect Influencer Fraud
You should go through the following steps each time you check an influencer's account:
- Run through the person's list of followers; and look for any distinct bad and inflated followers
- Check the likes of the last 12 posts of the influencer, for anything unusual
- Check the comments on those posts, and look at the pages of the accounts that wrote them.
Variations in Fraud-Free Influencers by Country
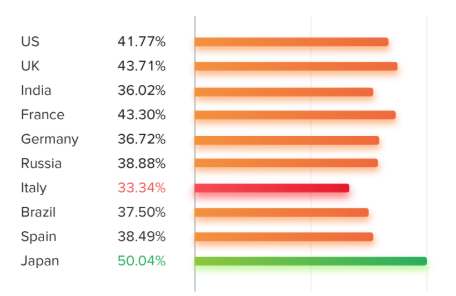
Although there aren't massive variations in fraud-free accounts between countries, there is still a reasonable gap between the best country (Japan) and the worst (Italy). It is perhaps concerning that even in Japan, only half the so-called influencers run fraud-free accounts. In Italy, only one-third of the "influencers” are fraud-free.
Audience Quality Score
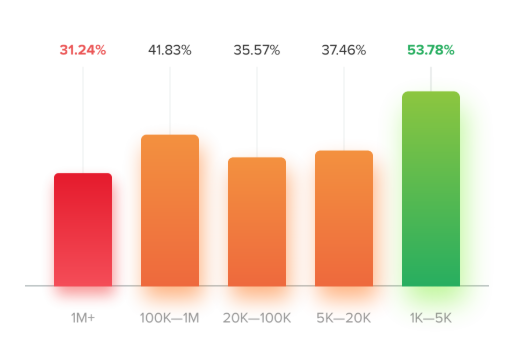
It is probably not a great surprise to find that the most significant accounts are the ones most affected by fraud. Conversely, the nano-influencers surveyed tended to the people most likely to be fraud-free.
The large accounts probably suffer from the sheer volume of spam. They usually don’t have the time to vert all of their followers, and some “rubbish” accounts slip through the net.
HypeAuditor also noted the relatively small number of fraud-free accounts with between 20K and 100K followers. They believe this is a reflection of inauthentic methods of Instagram growth.
Abnormal Growth
Most influencers increase their number of followers gradually. Sure, there can be some spurts in follower growth thanks to some promotion methods, advertising, mentions in media or a shoutout from another influencer, but as a whole, all fraud-free accounts show a similar pattern.
Some people cheat and use inauthentic ways to gain followers, however. Accounts that increase their follower numbers artificially will show sudden rises and “hockey-stick” growth on a Followers graph.
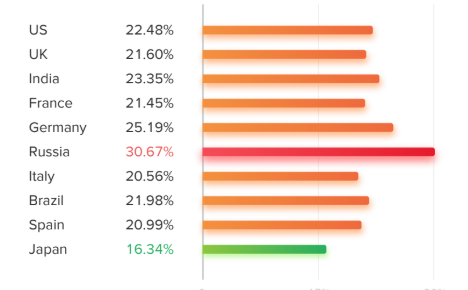
This is particularly evident in Russia, where more than 30% of their influencers use inauthentic measures to gain followers. These include buying followers and participating in “loop giveaways."
The effect is even more evident when you compare different sized accounts.
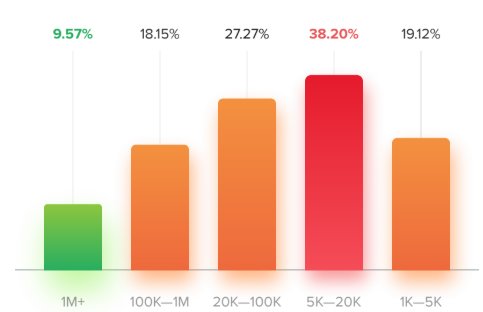
Here, you can see that the worst offenders are those who have just broken out of the nano-influencer zone. Many buy followers to kick-start the growth of their accounts. The mega-influencers and celebrities, however, gain followers by more organic methods.
Using Follower/Unfollower on Instagram
There’s a common trick used by “influencers” on Instagram to gain mass followers. You follow a three-step process:
- The influencer follows somebody, often also liking or commenting on one of their posts
- The person follows the influencer in return
- The influencer then quietly unfollows the person in a couple of days
The influencers use special tools to automate this Follow/Unfollow process.
You can spot somebody who used this process because they tend to have spikes in their Number of Followers graph over a time period.
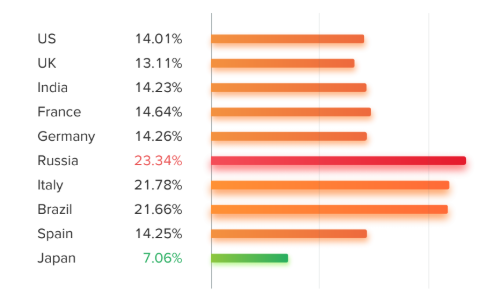
This Follow/Unfollow practice is particularly common in Russia, although less so in Japan.
Inauthentic Comments
There is only value in a comment if it is made with genuine intent, and has something worthwhile to say. Comments to tag-to-win giveaways and contests, spammy comments, and comments that come from Instagram Pods are inauthentic. Comments that consist of only emojis or words like "wow," "cool," and "fantastic" are of very little value. Other useless comments are often monosyllabic, dull, and irrelevant. Some comments even merely consist of a one-word mention of another account.
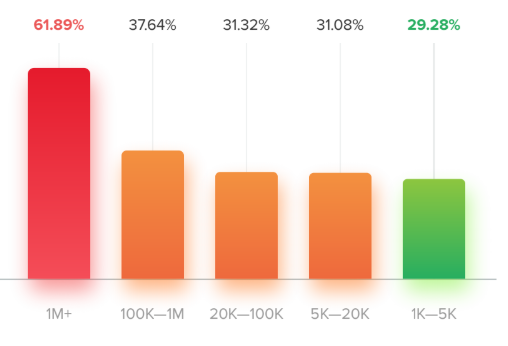
It is clear from the following graph that the largest accounts are the worst offenders at making meaningless comments. This is often because some employ spam methods that use other influencers and Instagram users to grow their accounts.
Comment Pods
Sometimes bloggers group together to create a comment pod. They gather on the social network chats (or other specialist chats like Discord) and comment on each other's posts.
These comments are harder to spot than other fake comments because real people write them; many may be well-written.
They tend to be more favored by smaller influencers because being part of a comment pod is still a manageable task for them. Once your account grows in size, this method becomes less effective.
Automatic Likes
Automatic likes are one of the more common types of fake engagement. You will often find less reputable businesses offering to sell likes, and can even see people advertising the service on places like Fiverr.
Many of these likes come from fake bot accounts. It is usually easy to spot these accounts. They are often private accounts with few photos and a near-empty bio. Sometimes they may even have strange account names – just a random mix of numbers and letters.
Accounts that buy automatic likes tend to have an almost identical number of likes on every post they make. Often they have very high engagement rates – much higher than the norm.
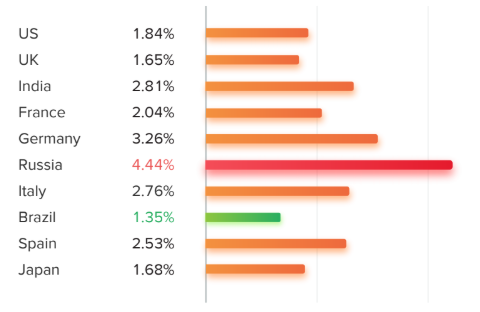
As you can see, Russia has by far the biggest problem with automatic likes, with Brazil having the smallest number.



