How much of social media marketing will still be in human hands three years from now? And what happens to brand voice when AI begins writing, designing, and even conversing on our behalf?
These questions are no longer theoretical. Platforms like Meta are moving toward fully automated campaigns, TikTok is experimenting with AI-driven avatars, and Pinterest is doubling down on visual search. Across the board, AI is rewriting the rules of content creation, targeting, engagement, and measurement.
Social AI is shifting the role of marketing from execution to stewardship. The challenge isn’t whether to adopt these tools — it’s how to guide them, set guardrails, and ensure authenticity at scale.
This guide explores the building blocks, opportunities, and risks of Social AI, equipping brands and agencies with the tools and tactics to compete in a landscape where algorithms are the new creative partners.
Functional Building Blocks of Social AI
At its core, Social AI can be broken down into several categories that operate across the content and campaign lifecycle:
Generative AI
On social platforms, generative AI is fueling the content engine. Marketers use tools that draft captions in brand voice, remix long-form webinars into TikTok and YouTube-friendly edits, or generate dozens of image and video variations for A/B testing.
Instagram’s built-in AI background editing and TikTok’s emerging AI video creation tools show how platforms are embedding these capabilities directly into creative workflows. The result is faster pipelines and more tailored creative that matches the speed of the feed.
Predictive & Prescriptive Analytics
Analytics in social is no longer about looking backward. Predictive models are used to anticipate which influencer partnerships will drive engagement, forecast the ROI of boosting a Reel vs. a TikTok, or suggest the optimal time to launch a campaign.
Meta’s Advantage+ Shopping campaigns, for example, already prescribe how to rebalance budgets across audiences and placements, letting AI handle optimization in-flight.
Recommendation Algorithms
These are the beating hearts of social platforms — TikTok’s “For You” page, Instagram Explore, and YouTube’s homepage. For brands, understanding recommendation engines means tailoring content to signal the algorithm rewards, such as early engagement velocity or watch time.
Optimizing for recommendation AI isn’t optional; it determines whether content disappears or reaches millions.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
In social, NLP powers sentiment analysis, social listening, and community management. Tools like Brandwatch and Sprinklr use NLP to parse millions of comments and posts in real time, surfacing micro-trends or spotting potential PR crises. Brands can also apply NLP to automate community responses at scale, ensuring that customer interactions feel timely and on-tone without requiring human monitoring 24/7.
Conversational AI
In social contexts, conversational AI is about extending dialogue at scale. Instead of limiting interaction to one-way broadcasts, brands can maintain ongoing conversations through automated systems that respond in real time.
Whether answering questions in comments, holding casual exchanges, or simulating personality-driven interactions, conversational AI gives social presences a sense of immediacy and responsiveness that is difficult to achieve manually.
Computer Vision & Recognition
The visual nature of social platforms makes computer vision central. It allows systems to understand what’s happening inside photos and videos — identifying products, recognizing unsafe content, or enabling augmented layers like filters.
For marketers, this means content can be made interactive, shoppable, and safer, with visuals not just displayed but interpreted and acted upon in real time.
These building blocks aren’t isolated silos — they overlap. A campaign that uses generative text for ad copy might also rely on predictive analytics for spend optimization and NLP for monitoring reactions.
Evolution of Social AI
The story of Social AI has three phases:
- Automation Phase (2010–2016): Tools like Buffer and Hootsuite automated scheduling.
- Algorithmic Phase (2016–2020): Social feeds shifted from chronological to algorithm-driven, making AI the invisible gatekeeper of reach.
- Generative Phase (2020–present): AI moved into the foreground. Platforms rolled out in-app editing, brands experimented with synthetic creators, and users embraced AI filters and co-pilots.
This trajectory signals that AI in social isn’t just about distribution anymore — it’s part of creation and engagement itself.
Takeaway
Social AI is not a monolith. It’s an ecosystem spanning generative tools, predictive analytics, and platform algorithms. Marketers who understand the layers — platform, brand, and user — can better navigate the opportunities and risks of this rapidly evolving environment.
How Brands & Marketers Use AI in Social Media
Social AI is no longer confined to experiments or pilot programs. For many marketers, it has become the hidden engine behind creative workflows, campaign execution, and audience engagement.
Understanding the tactical uses reveals where the real competitive edges are forming — and how brands can avoid being left behind.
Content Ideation and Trend Discovery
AI has transformed the earliest stage of the content cycle: figuring out what to make.
Instead of relying solely on human intuition, marketers now use AI-driven tools to surface trending topics, identify emerging hashtags, and analyze cultural conversations.
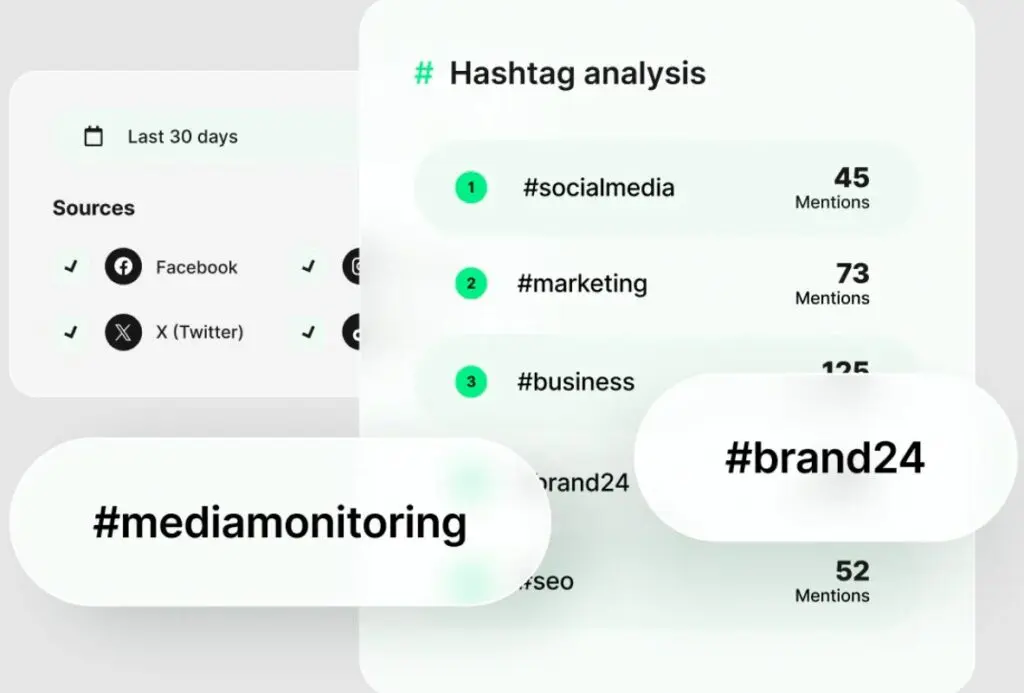
For example, a beauty brand might use Brand24 to monitor hashtag trends like #cleanbeauty or #skinfluencer, letting them spot a surge in usage days before it becomes mainstream. Brand24’s AI-powered “Anomaly Detector” can even surface why a hashtag suddenly spiked in reach.
At the same time, marketers are turning to ChatGPT for content ideation itself. Given a prompt about a campaign vertical or customer persona, ChatGPT can generate dozens of content angles, hooks, or thematic ideas in seconds — helping agencies break past creative blocks and get ahead of trends.
This allows agencies to position clients within trends before they peak, rather than after the moment has passed.
Creative Development and Asset Production
Generative AI is increasingly embedded in content production. Marketers use it to:
- Draft captions tailored to specific audience segments.
- Generate multiple visual variants of a single campaign theme.
- Repurpose long-form assets into short-form formats like TikTok or YouTube Shorts.
The value is not just speed, but also creative breadth. A single photoshoot can yield dozens of AI-enhanced derivatives, extending the shelf life of original content and allowing for targeted experimentation across demographics and platforms.
Scheduling, Orchestration, and Distribution
Beyond creation, Social AI automates when and where content is delivered. Smart scheduling systems analyze audience engagement patterns to post at optimal times, even adjusting dynamically if trends shift.
For brands managing multiple accounts across markets, orchestration tools can stagger launches, localize assets with AI translation, and balance campaign pacing without manual oversight.
A clear example comes from DigiTech Solutions, a digital marketing agency that used Predis.ai to unify content creation and scheduling in a single platform — eliminating tool switching and enabling the team to manage more campaigns with less overhead.
Similarly, agencies adopting Ocoya have leaned on its AI agents to automate cross-platform posting, even generating localized versions of assets so launches can roll out region by region without manual intervention.
Audience Targeting and Personalization
Marketers are moving from broad targeting to micro-personalization, enabled by AI. Platforms like Meta and TikTok already use AI to predict user interest, but brand-side tools layer on custom models.
For example, a fashion retailer might automatically generate ad creative variations for students, professionals, and parents — each with tailored messaging and imagery. This “audience-first” creative production would be impossible to scale manually.
A concrete case comes from Albert.ai, which helped a large retailer run paid social campaigns with autonomous audience optimization. In one retail personalization campaign, Albert delivered +64% improvement in ROAS over human-managed control campaigns by dynamically matching creatives and audience segments across products and messaging.
By continuously testing combinations of creative, copy, and audience segments, tools like Albert can identify which message resonates best with each micro-segment — then shift spend in real time. In practice, this means your “students vs. professionals vs. parents” variants don’t just exist — the system learns which variants work best for which segments and adjusts automatically.
Ad Optimization and Predictive Budgeting
In paid media, AI is used to run thousands of creative combinations and automatically prioritize winners. Real-time predictive modeling helps marketers allocate spend toward the ads, influencers, or audiences most likely to drive conversions. Rather than waiting for mid-campaign reports, AI enables near-instant adjustments, reducing wasted impressions and improving return on ad spend.
Major social media platforms are already providing built-in AI to support this. Meta’s Campaign Budget Optimization (CBO) and newer Advantage+ suite automatically shift spend across ad sets, steering budget toward ads showing early performance lift instead of relying on manual adjustments.
@daradenney #MetaPartner Three Things Businesses Need to Know About Meta’s Advantage+: 1. It’s CRAZY powerful. It uses AI to automate targeting, creative, placement, and even budget. It’s taken my time in ad accounts WAY down so I can concentrate on strategy and creative with my clients. 2. You can use Advantage+ shopping campaigns to drive online sales and Advantage+ app campaigns to drive app installs, both with the same AI juice. 3. There’s also Advantage+ Creative that can automate image editing, optimize copy and text, and even choose the right song for the right user. Have you tested out any Advantage+ on your campaigns? Let me know in the comments 🙂 @meta @Facebook
On TikTok, the Smart Performance Campaigns and tROAS bidding tools apply similar logic, using machine learning to distribute spend toward placements most likely to generate revenue, while also testing creative variants along the way.
@triomediauk TikTok’s making things easier for advertisers with a new automated ad process called Smart Performance Campaigns Find out more 👆 #digitalmarketingnews #digitalmarketingtips #tiktok #tiktokmarketing #leedsbusiness
Together, these systems show how predictive modeling isn’t just a theoretical benefit — it’s an embedded feature of today’s social ad platforms, giving marketers an always-on optimization layer that works faster than human media buying ever could.
Social Listening and Reputation Management
AI-powered sentiment analysis allows brands to track how audiences react not only to their campaigns but also to broader industry conversations. Marketers use this to identify potential crises early, evaluate the effectiveness of influencer partnerships, or understand which campaign themes resonate most.
In high-stakes verticals like finance or healthcare, this real-time monitoring can safeguard brand equity.
A strong example comes from the University of Glasgow, which partnered with Neon Caffeine to deploy Brandwatch during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. By monitoring sentiment across students, staff, and prospective applicants, the university used Brandwatch’s Signals and Alerts to detect potential reputational risks early and adjust communications in real time.
This always-on crisis management approach allowed their social team to deliver timely insights to leadership, refine messaging, and respond effectively to community concerns — ensuring communications remained aligned with audience sentiment during a highly volatile period.
Conversational AI and Customer Engagement
Brands are experimenting with AI agents that respond to DMs, comments, or live chat at scale. In TikTok Shop or Instagram DM commerce, conversational bots can answer product questions, recommend bundles, and even upsell. While human oversight is essential, these systems extend customer service into spaces where brands previously struggled to engage efficiently.
On platforms like Instagram and Facebook Messenger, Meta’s built-in Click-to-Message Ads and Automated Responses allow brands to trigger AI-powered conversations directly from ads or posts. These native tools can greet customers, suggest products based on past interactions, and provide quick-reply options that mimic human dialogue, all without requiring external integrations.
@j0nnym0 #greenscreen messaging-based transaction behavior via #whatsappbusiness is growing gangbusters internationally…click to message ads on meta helping further scale. Curious what the trajectory begins to look like (if much at all) in the US #facebookads #instagramads #socialmediamarketing #zuckerberg
For marketers, this means the customer journey stays entirely within the app, reducing drop-off points and keeping engagement frictionless.
TikTok Shop has also leaned into conversational AI by embedding smart chat assistants that interact with shoppers inside the checkout flow.
These bots can recommend complementary items, surface limited-time deals, and answer FAQs on shipping or returns in real time. Because these features are native to TikTok, they don’t feel like external interruptions — instead, they merge seamlessly with the social shopping experience, increasing the odds of conversion.
Influencer Discovery and Campaign Matching
Influencer marketing is another area where AI has a decisive role. Platforms now use machine learning to assess creator relevance, audience authenticity, and brand fit. Instead of manually reviewing hundreds of influencer profiles, marketers can rely on AI systems to shortlist candidates whose audiences mirror the brand’s target segments — cutting weeks off campaign planning cycles.
Dedicated influencer marketing platforms like Upfluence make this process more efficient by analyzing millions of creator profiles across platforms and applying Jayce AI to flag the best matches based on audience demographics, engagement rates, and brand safety indicators.
A strong example comes from Marriott Bonvoy, which partnered with Upfluence to collaborate with niche creators across TikTok and Instagram. By using Upfluence to identify high-engagement creators aligned with different travel lifestyles — from pet-friendly stays to luxury getaways — Marriott was able to diversify its storytelling across its 30+ hotel brands.
The campaign generated over 11 million in cumulative reach, nearly 2.7 million engagements, and 489 pieces of creator content, all while optimizing cost per view to just $0.02 — well below industry benchmarks.
Measurement and Performance Insights
The final application is attribution and measurement. Social AI helps marketers model the impact of each touchpoint — ad view, influencer post, organic mention — across the customer journey. By running predictive “what-if” scenarios, brands can forecast how reallocating spend or adjusting creative mix might influence sales, allowing for more confident decision-making.
Takeaway
Brands and agencies use Social AI across the full campaign lifecycle — from ideation to optimization. Those who embrace it see efficiency gains, sharper personalization, and faster insights. Those who don’t risk relying on outdated, manual processes while competitors scale campaigns that are both smarter and faster.
Benefits, Trade-offs & Challenges
AI on social media opens doors to new capabilities — but those come with new responsibilities. Below is a reframed exploration, grounded in what’s actually unfolding on platforms like TikTok and Meta (Instagram / Facebook), focusing on features, tensions, and real risks.
Efficiency, Automation & Creative Leverage
One of AI’s most visible benefits in the social domain is in automating creative and distribution workflows. Meta has rolled out generative AI features inside Ads Manager / Advantage+, enabling advertisers to automatically produce creative variants — image-to-video transformations, sticker overlays, dynamic branding — reducing time and creative bottlenecks.
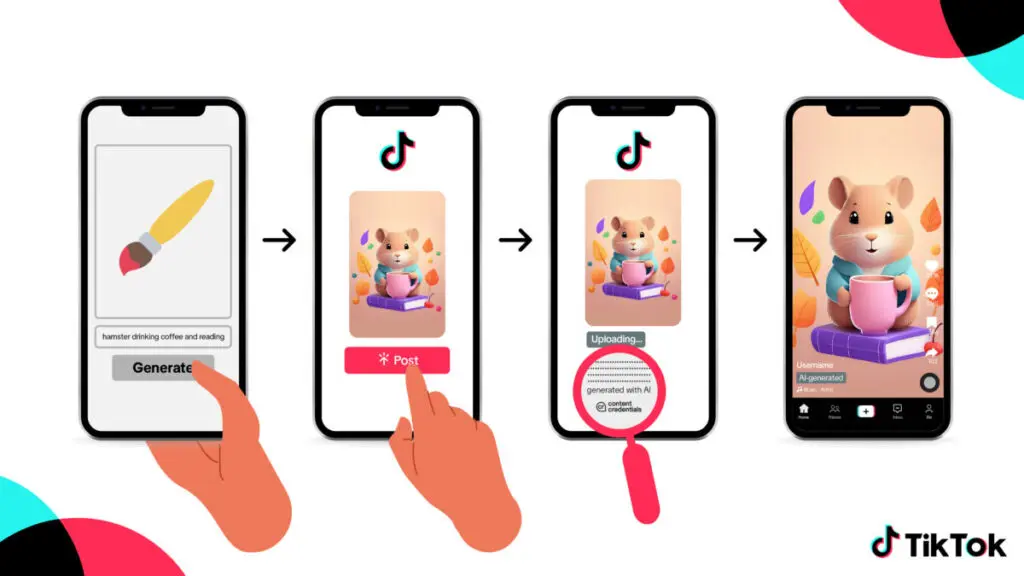
Likewise, TikTok has introduced tools such as AI Alive, which animates static images within Stories with facial expressions or subtle motion — turning still visuals into engaging video-like content. Each piece carries a “Made with AI” label, enhancing transparency.
@shou.time Have you tried #tiktok AI Alive? It takes your pictures and converts them into videos using a text prompt. US users can now access this feature through the Story Camera
These native tools let social marketers experiment at scale — without leaving the platform ecosystem or relying on pieced-together external pipelines.
Personalization vs. Homogenization
AI excels at tailoring content to micro-segments. But one paradox is that as many brands adopt the same AI templates, the result can feel formulaic. Two risks emerge:
- Content convergence: If all brands use the same AI toolkits and base prompts, user feeds begin to look stylistically indistinct — making it harder for any one brand to stand out.
- Diminishing returns on novelty: Audience attention is drawn to what feels new or human, not what feels like algorithmic sameness.
To help counter that, TikTok has begun automated labeling of AI-generated content, including metadata tagging for synthetic uploads, using C2PA standards.
This pushes brands to differentiate not just in content but in intent, tone, and narrative authenticity.
Brand Safety, Deepfakes & Truth Risk
Social AI tools make it easier to generate compelling visuals or mimic voices — but that also means the risk of deepfakes, identity theft, and impersonation is rising fast.
On TikTok, for instance, deepfake “doctors” have been used to promote bogus medical cures, blending synthetic faces and authoritative-sounding scripts to mislead audiences. These so-called "doctors" have made the national news across the U.S. and the UK in recent years.
@itvnews Deepfake content of some of Britain's most recognisable television doctors is being shared on social media to sell scam products, the British Medical Journal (BMJ) has found #itvnews #health #tech
Because these impersonations appeared credible, many users did not question their authenticity, showing how easily deepfakes can erode trust in sensitive verticals like health and wellness.
For brands, the danger is twofold: they risk being directly impersonated by deepfakes or indirectly harmed when such content circulates in their industry. The cost of “seeming AI-generated” goes beyond backlash — it undermines credibility at a time when trust is already fragile on social platforms.
Dependency, Bias & Data Quality
AI models are only as good as their training data. If marketers depend blindly on AI-generated insights, they risk reinforcing blind spots or biases (e.g. demographic or creative stereotypes). The more you offload decisions, the smaller the margin for human intuition, especially when edge cases arise — controversial posts, regional sensitivities, cultural nuance.
Also, over-reliance creates fragility: platform changes, API limits, or shifts in model weights can upend your operations if your pipelines are too tightly coupled to them.
The brands that succeed will treat AI in social not as a weapon of volume but as a scalpel of insight. That means layered oversight:
- human review on high-value posts
- prompt audits and bias checks
- content audits for nuanced voice alignment
- fallback rules (e.g. never auto-post in a crisis window)
AI should accelerate responsiveness — not replace thoughtfulness.
5 Emerging / Future Trends to Watch
The next frontier of Social AI will push past incremental improvements and into structural reinvention — new paradigms of how social content is created, surfaced, and experienced. Below are some of the major trends we see gaining traction, along with nascent features or experiments worth keeping an eye on.
1. Full Campaign Automation by Platforms
One of the boldest shifts on the horizon is platforms taking over the end-to-end campaign orchestration process. Meta, for instance, is reportedly working toward fully automating advertising by 2026 — meaning brands could drop in a product image and a budget, and AI handles creative generation, targeting, bidding, and optimization.
If realized, this will further compress the gap between strategy and execution. Marketers will need to reorient their role toward oversight, guardrails, and brand voice design — even more than hands-on tactical control.
Meta’s plan goes far beyond today’s optimization features. The company wants a system where copy, visuals, and targeting are all produced by AI, tested in real time, and auto-adjusted for different audiences. A single campaign could be rendered dozens of ways — snowy landscapes for Denver users, palm trees for Miami — without marketers lifting a finger.
This opens the door to hyper-personalization at scale but raises concerns over creative consistency and brand identity.
The upside is clear for small and midsize businesses that lack agencies or in-house teams, but larger advertisers may see it as ceding too much control. The likely outcome is a shift in marketer responsibilities: away from manual campaign building and toward AI stewardship — guiding prompts, monitoring outputs, and stepping in when human creativity or cultural nuance is essential.
2. AI-Generated Influencers & Virtual Avatars
AI-generated influencers or virtual avatars are already here. But their use, so far, has been sporadic.
Still, the examples are starting to multiply. Brands like Mango have launched fully virtual brand ambassadors that act as spokespeople for product lines, published across Instagram and TikTok as part of their digital storytelling.
@suhailgamify Mango launches AI generated marketing campaign @Mango #ai #marketing #advertising #aiimages #artificialintelligence #mangocommunity
In another example, virtual influencer Lu do Magalu leads the Brazilian fashion scene. The influencer is created by the retailer Magazine Luiza, which has entered into partner campaigns with major brands like Samsung, Red Bull, and MAC , and acts as a bridge between AI identity and real product promotion.
On TikTok, the avatar or AI influencer format is evolving. Vodafone recently ran a TikTok ad campaign in Germany featuring an AI-generated presenter, which drew controversy over uncanny facial artifacts (hair moves too smoothly, disappearing moles) — signaling that brands are testing how far AI can play “real person” before users push back.
@leandrenash Are Brand AI influencers crossing the line ? Vodafone has confirmed the host is 100% AI, and they are not the only brand to work with virtual influencers. However, the data shows that only 23% of consumers engage with AI influencers, and nearly half don't trust them. This raises questions about the future of advertising and whether brands are crossing a line with the use of virtual influencers. #tiktok #aiinfluencer #virtualinfluencer #vodafone #advertising
The experiment shows that TikTok is open to content where the “creator” may not be human, and that avatars can serve as presenters, narrators, or product endorsers in-feed.
As these avatars grow more lifelike and capable — with voice, gesture, and content adaptation — brands may increasingly choose them for 24/7 consistency, controlled branding, or reaching audiences in new digital-first formats. The trade-off: maintaining authenticity, ensuring disclosure, and preventing overuse so that audience trust doesn’t erode.
3. Contextual Commerce & Object Recognition (AI Visual Shopping)
Social commerce is growing more embedded and intelligent. AI-powered systems are improving at recognizing objects in video frames and linking them to products — turning nearly every visual moment into a potential storefront.
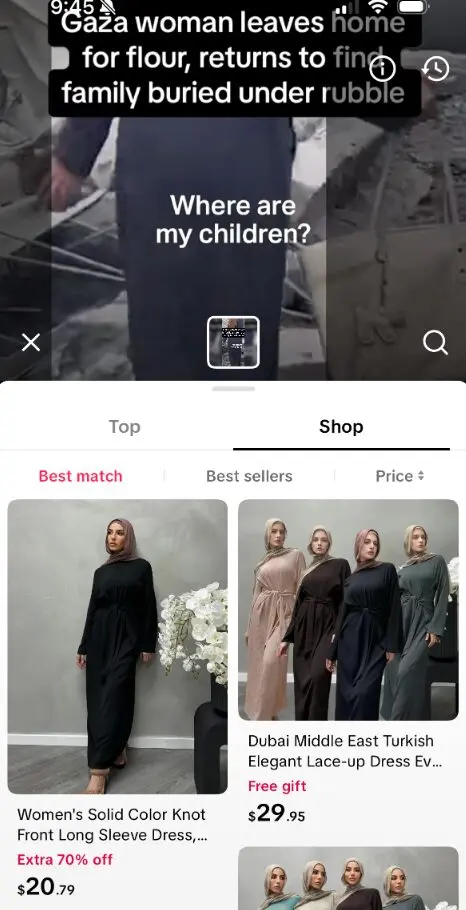
That said, missteps can be glaring. Recently, TikTok’s visual recognition engine tagged distressing Gaza footage with product suggestions (e.g. clothing items shown) — an example of why context sensitivity is vital.
But not all AI visual shopping is controversial. Pinterest, for example, has leaned into AI-powered discovery with its new visual search tools that let users long-press on any Pin to initiate a product search.
Instead of relying on keywords, Pinterest’s AI decodes images to identify styles, colors, and fabrics, then suggests shoppable results tailored to each user’s preferences.
According to VP of Design Dana Cho, the goal is to deliver not just search results but a “personalized journey of discovery” that blends inspiration with direct purchasing.
For marketers, this means more sophisticated customer journeys: a user admiring a Y2K outfit can instantly refine by color or occasion and surface a brand’s product catalog that matches the look. While TikTok’s misstep shows the risks of blunt AI recognition, Pinterest demonstrates how a more curated, visual-first approach can improve discovery, fashion shopping, and ultimately conversions.
In the future, smarter models may better distinguish tone, subject matter, and context to avoid such misfires while enabling seamless “tap-to-buy” overlays in reels, stories, or live video.
4. AI Agents as Social Co-Creators and Moderators
Beyond chatbots, we’ll see more autonomous AI agents that “inhabit” social presences. These agents might propose post concepts, respond to comments in brand voice, or mediate community interactions.
On the moderation side, AI agents could preemptively flag harmful or misleading posts, escalate issues to humans, or enforce content policies with minimal manual intervention. The goal: scalable, always-on moderation that doesn’t rely solely on manual review or reactive response.
5. Predictive Creative & Trend Forecasting
While brands already use trend-prediction tools, the next generation will get proactive: AI that not only identifies rising memes or audio trends, but also generates content primed to match them before they even fully emerge.
Some platforms and third-party tools already boast early versions of this kind of forecasting pipeline, analyzing millions of micro-interactions to flag “themes about to go big.”
Tools like Trendalytics already use AI to scan search behavior and social chatter to flag rising fashion and consumer trends before they peak.
Similarly, Heuritech applies computer vision to Instagram and TikTok content to predict which colors, shapes, or styles are set to trend, helping brands design and publish content in advance. These early examples show how predictive creative is shifting marketers from chasing trends to preparing content ahead of them.
In practice, this means brands may begin publishing content ahead of trends rather than reacting, gaining “first-mover” positioning.
Steering the Future of Social AI
Social AI is no longer a distant concept — it is the backbone of how platforms shape feeds, how brands reach audiences, and how users engage with content. From Meta’s push toward fully automated campaigns to Pinterest’s AI-powered visual shopping, the direction of travel is clear: AI is becoming a default layer across every touchpoint in social media.
For marketers, this shift is both liberating and daunting. On one hand, AI unlocks efficiency, personalization, and scale at levels previously impossible. Campaigns can be launched in hours, tailored in real time, and adapted across markets without ballooning production budgets. On the other, the trade-offs are real. Deepfakes, brand voice dilution, and the risks of “AI slop” highlight that automation without oversight can erode trust faster than it builds reach.
The opportunity lies in adopting an AI stewardship mindset. Rather than viewing AI as a replacement for creative and strategic teams, marketers should see it as an amplifier. That means guiding automated outputs with strong brand guardrails, refining campaigns with human nuance, and stepping in when cultural moments require judgment no machine can provide.
As platforms embed AI deeper into their ecosystems, the winners won’t simply be the first to adopt every new tool. They’ll be the ones who know when to automate, when to personalize, and when to bring back the human touch. In a social landscape where attention and trust are fragile, the brands that master this balance will define the future of digital marketing.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI changing the way brands manage multiple social accounts?
Many businesses now rely on AI social media marketing software to automate scheduling, track engagement, and analyze performance across platforms, reducing manual workload and improving consistency.
What are some practical AI tools marketers should start with?
Marketers often begin with AI marketing tools that handle campaign optimization, predictive analytics, and automated reporting, allowing teams to focus more on creative and strategy.
Can AI really generate original social media content?
Yes, today’s AI content creation software can write captions, design visuals, and even edit videos, enabling brands to keep up with fast-moving platform trends without overwhelming internal teams.
How does AI influence the way brands choose influencers?
Brands increasingly turn to AI influencer marketing systems that analyze audience authenticity, engagement rates, and demographic data to identify creators most likely to drive real results.
What role does AI play in overall social media strategy?
AI is now central to AI social media strategies, from algorithm-friendly creative production to data-driven ad targeting, giving brands an edge in reaching the right audiences.
Is it possible to build a virtual influencer from scratch?
With today’s tools, brands can learn how to create an AI influencer, developing digital personas that engage followers just like human creators.
Which platforms help manage large-scale AI influencer programs?
Specialized AI influencer marketing platforms provide campaign management dashboards, automated performance tracking, and scalable workflows for brands running multiple creator partnerships.
Are there any moves toward AI-native social networks?
Experiments like an OpenAI social media network show how AI could power platforms where recommendation systems, moderation, and even community dynamics are driven by generative models.