Ever wondered what an Amazon fulfillment center is? If you’re an Amazon seller or are planning to sell on the marketplace, you may be curious to learn how the retail giant’s fulfillment centers work. By getting a better idea of what these fulfillment centers are and how they work, you can get a clearer picture of the role they play in your business and the value they add to your bottom line.
In this guide, we take you on a tour of Amazon fulfillment centers and help you navigate how they work and where they’re located. Let’s get started.
What is an Amazon Fulfillment Center? – An In-Depth Tour of Amazon Fulfillment Centers:
What is a Fulfillment Center?
Before we dive too deep into Amazon fulfillment centers, let’s first try to understand what a fulfillment center is. A fulfillment center is a facility that takes care of the order fulfillment process. Sometimes considered a packing warehouse, the fulfillment center receives customer orders, picks them from the storage location, packs them, and ships them out to be delivered to the end customer.
What are Amazon Fulfillment Centers?
As the name suggests, an Amazon fulfillment center is a facility in which orders placed on Amazon are processed and fulfilled. They store inventory and function as distribution centers through which orders are received, processed, picked, packed, and shipped out. Amazon fulfillment centers are responsible for fulfilling all orders for Amazon products and all Fulfillment by Amazon orders.
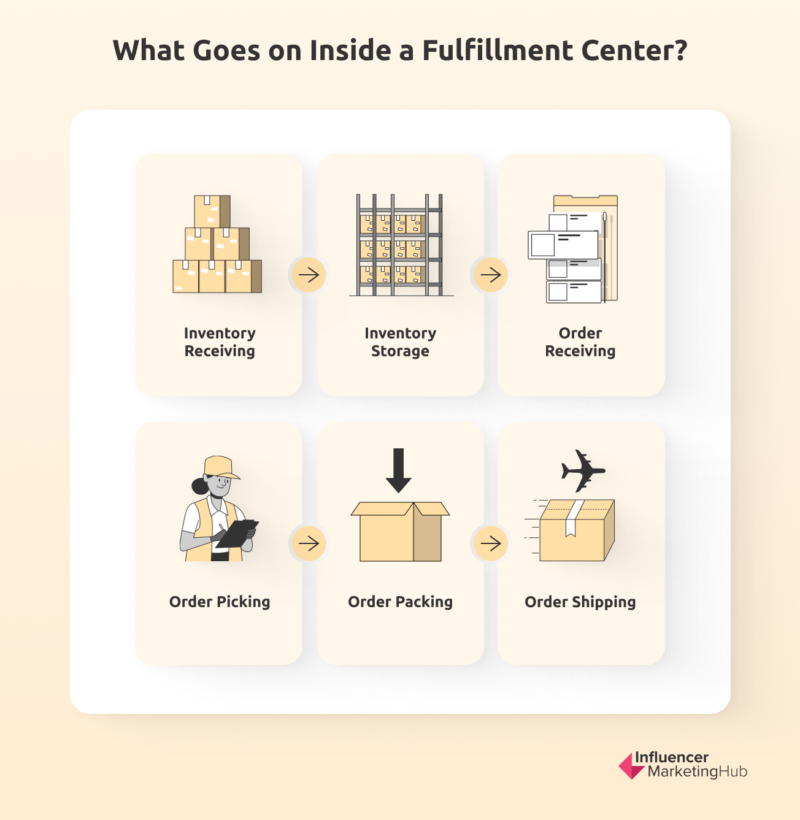
Activities Within a Fulfillment Center?
There are a number of activities that take place within a fulfillment center. Typically, the following processes are carried out by a fulfillment center.
Inventory receiving
First, the fulfillment center receives the inventory. Products enter the warehouse through the inbound dock typically using forklifts or sometimes manually built into pallets. In an Amazon fulfillment center, the freight is also separated between those coming from another Amazon facility and those coming from a vendor.
In the latter case, the products would come from a seller that’s using the Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program. This service allows sellers to send their inventory to Amazon fulfillment centers, where they’re stored until they’re ready to be shipped out. Once orders are placed on the website, the fulfillment center then picks, packs, and ships the orders in addition to taking care of customer service.
Inventory storage
The received inventory is then stowed within the fulfillment center until they’re ready to be fulfilled. This stowing process varies depending on the company. While others may have a system in place to store items by product type and category, others may also store them based on product type.
At Amazon fulfillment centers, all the stowed items are properly recorded using computers and barcode scanning. This allows associates to keep track of where specific items are located within the fulfillment center.
Order receiving
Once an item is processed and stowed in the fulfillment center, it’s made available for purchase on the seller’s website. In the case of Amazon, the item will be available for purchase on the Amazon website. Then when a customer places an order for the item, the fulfillment center automatically receives and processes the order.
Order picking
After the order is processed, picking lists are generated and assigned to pickers. It’s the job of these pickers to ensure that the right items are sent out to the customers. The picking process also varies depending on the fulfillment center.
At Amazon, for instance, a robot will bring pods filled with items to pick stations, where associates have to retrieve the right item from the bin. The picked items are then set aside for the next stage of the fulfillment process.
Order packing
The next step involves packing orders and getting them ready for shipping. Associates will start by scanning items for accuracy and organizing them based on which shipment they belong to. The items are then sent to pack stations, where associates will place them inside appropriate boxes and pack them properly to withstand transportation.
At Amazon fulfillment centers, the process is optimized to minimize waste as much as possible. They use a system that recommends the correct box size for each item or shipment. It also measures the exact amount of tape that’s required so that nothing goes to waste.
Order shipping
Once packed, orders go through a final preparation process wherein they’re weighed and assigned shipping labels. The specific activities that take place during this stage also vary for different companies.
Amazon leverages SLAM (scan, label, apply, manifest) machines across their fulfillment centers. These machines apply shipping labels to the packages at extraordinary speed for increased efficiency. Each package is also weighed for quality control, which helps to ensure that the content matches the order.
At this stage of the fulfillment process, shipping sorters also play a crucial role by reading the package labels. They then determine where each order should be sent and how fast they should be sent out. The packages are then transported down slides and directed to the correct trailer depending on different criteria such as location, shipping method, and delivery speed.
Items will be distributed based on the transportation method relevant to the specified delivery speed. These methods may range from planes and Amazon trucks to carrier partners such as the U.S Postal Service.
For example, Prime orders will get priority shipping and, as such, diverted to transportation methods that can ensure faster deliveries. Planes are typically leveraged to meet the 2-day delivery window that Prime members are eligible to get. Amazon also leverages vans, bikes, and sometimes even robots to deliver orders to the end customers.
How Businesses Can Leverage Amazon Fulfillment Centers
Based on what we’ve outlined above, you can understand how Amazon leverages automation and technology to improve speed and accuracy across its fulfillment centers. Businesses selling on the website can leverage these fulfillment centers to scale their fulfillment operations and exponentially grow their business.
To take advantage of Amazon fulfillment centers, sellers will need to sign up for the Fulfillment by Amazon program. For a predetermined fee, they can send their inventory to Amazon fulfillment centers and leave the entire fulfillment process to the experts. This includes receiving orders, picking and packing them, and shipping them out. In addition, Amazon will also handle customer support on the seller’s behalf, which significantly saves you time and resources.
Amazon has a vast network of fulfillment centers spread across the globe, which further makes it an appealing choice. These fulfillment centers are strategically located near major metropolitan areas to speed up the shipping process. This means orders can get delivered quickly and at a lower cost.
Moreover, Amazon also has a diversified delivery fleet to optimize the shipping and delivery process even after orders leave their facility. From trucks and vans to bikes and planes and even robots–your orders will be assigned an appropriate transportation method depending on how soon they need to be delivered. That way, you can ensure a seamless delivery experience and maintain customer satisfaction.
Where are Amazon Fulfillment Centers Located?
If you’re interested in using Amazon fulfillment centers for your business, you may want to know where they’re located. By getting a clear picture of their locations, you’ll be able to better understand how these fulfillment centers can add value to your business. Here’s a complete list of all the fulfillment centers owned by Amazon within the United States to give you an idea of how you can leverage them.
Arizona
- #PHX3 – 6835 W. Buckeye Rd, Phoenix, AZ, 85043
- #SAZ1 – 3333 S 7th St, Phoenix, AZ 85040-1182
- #AZA5 – 6000 W Van Buren St, Phoenix, AZ 85043
- #TUS1 – 533 W Lower Buckeye Rd, Phoenix, Arizona, 85043
- #PHX6 – 4750 W. Mohave St, Phoenix, AZ, 8504
- #TUS2 – 6701 S. Kolb Rd, Tucson, AZ 85756
- #TFC1 – 5050 W. Mohave St, Phoenix, AZ 85043
- #UAZ1 – 500 S 48th St, Phoenix, AZ 85034
- #PHX7 & PHX8 – 800 N. 75th Ave, Phoenix, AZ, 85043
- #GYR1 – 580 South 143rd Avenue, Goodyear, AZ 85338
- #PHX8 – 800 N. 75th Ave Phoenix, AZ, 85043
- #GYR3 – 8181 W Roosevelt St., Phoenix, AZ 85043
- #VAZ1 – 3333 S 7th St., Phoenix, AZ 85040
- #PHX9 – 777 S 79th Ave, Tolleson, Arizona, 85353
- #PHX5 – 16920 W. Commerce Dr, Goodyear, AZ, 85338
Arkansas
- #LIT1 – 7001 Zeuber Rd, Little Rock, AR 72206
- #DLR1 – 1920 N Locust St, North Little Rock, AR 72114
- #LIT2 – 13001 US-70, North Little Rock, AR 72117
California
- #LGB1 – 2417 E. Carson St, Long Beach, CA 90810
- #SNA6/SNA9/DCA2 – 5250 Goodman Rd, Eastvale, CA 92880
- #PSP1 – 1010 West Fourth St, Beaumont, CA 92223
- #BFL1 – 1601 Petrol Rd, Bakersfield, CA 93308
- #DCA2 – 5250 Goodman Rd, Eastvale, CA 91752
- #LGB3 – 4590 Goodman Way, Building 1, Eastvale, CA 91752
- #LAX9 – 11263 Oleander Ave, Building 1, Fontana, CA 92337
- #FAT1 – 3575 S Orange Ave, Fresno, CA 93725
- #SJC7 – 188 Mountain House Pkwy, Tracy, CA 95391
- #OAK4/OAK6 – 1555 N. Chrisman Rd, Tracy, CA 95304
- #XUSD – 1909 Zephyr St, Stockton, CA 95206
- #SNA7/SNA8/LGB5/KRB1 – 555 East Orange Show Rd, San Bernardino, CA 92408
- #PCA2 – 1650 East Central Ave, San Bernardino, CA 92408
- #SCK1 – 4611 Newcastle Rd, Stockton, CA 95215
- #ONT2/3/4/7 – 1910 & 2020 E Central Ave. San Bernardino, CA 92408
- #SMF1 – 4900 W Elkhorn Blvd, Metro Air Park, Sacramento, CA 95835
- #LGB9 – 4375 N Perris Blvd, Perris, CA 92571
- #OAK3 – 255 Park Center Dr, Patterson, CA 95363
- #SNA4 – 2496 W Walnut St, Rialto, CA 92376-3009
- #LGB7 – 1660 N. Locust Ave, Rialto, CA 92376
- #LGB6 – 20901 Krameria Ave, Riverside, CA 92518
- #ONT9 – 2125 W. San Bernardino Ave, Redlands, CA 92374
- #LGB4 – 27517 Pioneer Ave, Redlands, CA 92374
- #ONT6/HLA3 – 24208 San Michele Rd, Moreno Valley, CA 92551
- #SMF3 – 4723 S B St, Stockton, CA 95215
- #SCK3 – 3565 N Airport Way, Manteca, CA 95336
- #DPS3 – 2405 Conejo Spectrum St, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
- #PCA1 – 1565 N MacArthur Dr, Tracy, CA 95376
Colorado
- #DEN3 – 14601 Grant St, Thornton, CO 80023
- #DEN5 – 19799 E 36th Dr, Aurora, CO 80011
- #DDV5 2889 Himalaya Dr, Aurora, CO 80011
- #DCS3 – 4303 Grinnell Blvd, Colorado Springs, CO 80925
- #DEN2 – 24006 E. 19th Ave, Aurora, CO 80019
Connecticut
- #BDL2 – 200 Old Iron Ore Rd, Windsor, CT 06095
- #BDL5 – 29 Research Parkway, Wallingford, CT 06492
- #BDL1 – 801 Day Hill Road Windsor, CT 06095
- #BDL3 – 415 Washington Ave, Building 3, North Haven, CT 06473
- #BDL4 – 1221 Kennedy Rd, Windsor, CT 06095
Delaware
- #PHL1 – 1 Centerpoint Blvd, New Castle, DE 19720
- #PHL7/PHL9 – 560 Merrimac Ave, Middletown, DE 19709
- #PHL3 – 1600 Johnson Way, New Castle, DE 19720
- #PHL8 – 727 N. Broad St, Middletown, DE 19709
Florida
- #MIA1– 14000 NW 37th Ave, Opa Locka, FL 33054
- #JAX5 – 4948 Bulls Bay Hwy, Jacksonville, FL 32219
- #TPA1 – 3350 Laurel Ridge Ave, Ruskin, FL 33570
- #MCO5 – 305 Deen Still Rd, Davenport, FL 33897
- #JAX2 – 12900 Pecan Park Rd, Jacksonville, FL 32218
- #TPA2/#LAL1 – 1760 County Line Rd, Lakeland, FL, 33811
- #UFL4/SFL1 – 7469 Kingspointe Pkwy, Orlando, FL 32819
- #MCO9 – 2841 Access Rd, Davenport, FL 33897
- #JAX3 – 13333 103rd St, Cecil Commerce Center, Jacksonville, FL 32221
- #MCO1– 12340 Boggy Creek Rd, Orlando, FL 32824
Georgia
- #MGE3 – 808 Hog Mountain Rd, Building F, Jefferson, GA, 30549
- #ATL7 – 6855 Shannon Pkwy S, Union City, GA 30291
- #PGA1 – 6200 Fulton Industrial Blvd, Atlanta, GA 30336
- #ATL6 – 4200 N Commerce Dr, East Point, GA 30344
- #SAV3 – 7001 Skipper Rd, Macon, GA 31216
- #MGE1/MGE7 – 650 Broadway Ave, Braselton, GA 30517
- #ATL8 – 2201 Thornton Rd, Lithia Springs, GA 30122
- #ATL2 – 2255 W Park Blvd, Stone Mountain, GA 30087
Idaho
- #BOI2 – 5319 E Franklin Rd, Nampa, ID 83687
Illinois
- #ORD9 – 23700 W Bluff Rd Bldg A, Channahon, IL 60410
- #HMW1 – 30260 Graaskamp Blvd, Wilmington, IL 60481
- #ORD2 – 23714 W Amoco Rd, Channahon, IL 60410
- #MDW5 – 16825 Churnovic Ln, Crest Hill, IL 60435
- #PIL1 – 801 Midpoint Rd, Minooka, Illinois 60047
- #STL4– 3050 Gateway Commerce Center Dr S, Edwardsville, IL
- #MDW4 – 250 or 201 Emerald Dr, Joliet, IL 60433
- #MDW7 – 6605 or 6521 W Monee Manhattan Rd, Monee, IL 60449
- #MDW6 – 1125 W Remington Blvd, Romeoville, IL 60446
- #DIL7 – 3601 Howard St, Skokie, IL 60076
- #MDW8 – 1750 Bridge Dr, Waukegan, IL 60085
- #STL6/STL7/HLU1– 3931 Lakeview Corporate Dr, Edwardsville, IL 62025
- #MDW9 – 2865 Duke Pkwy, Aurora, IL 60502
Indiana
- #PIN1 – 6161 Decatur Blvd, Indianapolis, IN 46241
- #DIN3 – #200, 5545 Chet Waggoner Ct, South Bend, IN 46628
- #SDF8 – 900 Patrol Rd, Jeffersonville, IN 47130
- #IND1 – 4255 Anson Blvd, Whitestown, IN 46075
- #IND7 – 9101 Orly Dr, Indianapolis, IN 46241
- #IND2/#IND3 – 715 Airtech Pkwy, Plainfield, IN 46168
- #IND5 – 800 S Perry Rd Plainfield, IN 46168
- #XUSE – 5100 S Indianapolis Rd, Whitestown, IN 46075
- #IND9 – 2140 Stacie’s Way, Greenwood, IN 46143
- #DIN1 – 5850 W 80th St, Indianapolis, IN 46278
- #IND4/IND8 – 710 South Girls School Rd, Indianapolis, IN 46214
Iowa
- #DSM5 – 500 SW 32nd St, Bondurant, IN 50009
Kansas
- #MCI5 – 16851 W 113th St, Lenexa, KS 66219
- #MKC6 – 6925 Riverview Ave., Kansas City, KS 66102
- #MKC4 – 19645 Waverly Rd, Edgerton, KS 66021
Kentucky
- #SDF9 – 100 W. Thomas P. Echols Lane, Shepherdsville, KY 40165
- #SDF1 – 1105 S Columbia Ave, Campbellsville, KY 42718
- #CVG8 – 7968 Kentucky Dr, Suites 2-3, Florence, KY 41042
- #SDF7 – 300 Omicron Ct, Shepherdsville, KY 40165
- #SDF2 – 4360 Robards Ln, Louisville, KY 40218
- #CVG1 – 1155 Worldwide Blvd, Hebron, KY 41048
- #SDF4 – 376 Zappos.com Blvd, Shepherdsville, KY 40165
- #LEX1/LEX3 – 1850 Mercer Rd, Lexington, KY 40511
- #CVG3 – 3680 Langley Dr, Hebron, KY 41048
- #CVG2 – 1600 Worldwide Blvd, Hebron, KY 41048
- #IVSB/#HCN1 – LogistiCenter 275 #2, 3521 Point Pleasant Rd, Hebron, KY 41048
- #LEX2 – 172 Trade St, Lexington, Kentucky, 40511
- #SDF6 – 271 Omega Pkwy, Shepherdsville, KY 40165
- #IVSA – 4620 Olympic Blvd, Erlanger, KY 41018
Maryland
- #DCA1 – 1700 Sparrows Point Blvd, Sparrows Point, MD 21219
- #HSE1 – 13905 Crayton Blvd, Hagerstown, MD 21742
- #HBA1 – 1100 Woodley Rd, Aberdeen, MD 21001
- #MDT2 – 600 Principio Pkwy West, North East, MD 21901
- #BWI2 – 2010 Broening Hwy, Baltimore, MD 21224
Massachusetts
- #BOS5 – 1000 Technology Center Dr, Stoughton, MA 02072
- #BOS7 – 1180 Innovation Way, Fall River, MA 02722
- #DBO2 – 500 Sprague St, Dedham, MA 02026
Michigan
- #DTW5 – 19991 Brownstown Center Dr, Brownstown Charter Township, MI 48183
- #DET2 – 50500 Mound Rd, Shelby Township, MI 48317
- #GRR1 – 4500 68th St. SE, Caledonia, MI 49316
- #DTW1 – 32801 Ecorse Rd, Romulus, MI 48174
- #DET1 – 39000 Amrhein Rd, Livonia, MI 48150
Minnesota
- #MSP1 – 2601 4th Ave E, Shakopee, MN 55379
- #MSP9 – 9001 Wyoming Ave N, Brooklyn Park, MN 55445
Mississippi
- #MEM6 – 11505 Progress Way, Olive Branch, MS 38654
- #MEM2 – 191 Norfolk Southern Way, Chickasaw Trail Industrial Park, Byhalia, MS 38611
Missouri
- #STL8 – 4000 Premier Pkwy, St. Peters, MO 63376
- #DLI1 – Hazelwood, MO 63042
Nevada
- #LAS1 – 12300 Bermuda Rd, Henderson, NV 89044
- #RNO3 – 555 Milan Dr, Sparks, NV 89434
- #LAS2 – 3837 Bay Lake Trail Suite 115, North Las Vegas, NV 89030
- #RNO4 – 8000 N Virginia St, Reno, NV 89506
- #LAS7 – 6001 E. Tropical Pkwy, North Las Vegas, NV 89115
- #LAS6 – 4550 Nexus Way, North Las Vegas, NV 89115
New Hampshire
- #BOS1 – 10 State St Nashua, NH 03063
New Jersey
- #EWR6/EWR7 – 275 Omar Ave, Avenel, NJ 07001
- #ACY1 – 240 Mantua Grove Rd, West Deptford, NJ 08066
- #EWR4 – 50 New Canton Way, Robbinsville, NJ 08691
- #LGA9 – 2170 State Route 27, Edison, NJ 08817
- #EWR9 & #LGA6 – 8003 Industrial Ave. Carteret, NJ 07008
- #ACY2 – 1101 E. Pearl St, Burlington, NJ 08016
- #TEB6 – 22 Hightstown-Cranbury Station Rd, Cranbury, NJ 08512
- #EWR1 – 50 New Canton Way Robbinsville, NJ 08691
- #EWR8 – 698 Route 46 West, Teterboro, NJ 07608
- #TEB3 – 2651 Oldmans Creek Rd, Logan Township, NJ 08085
- #LGA7 – 380 Middlesex Ave, Carteret, NJ 07008
New York
- #JFK8/DYY6 – 546 Gulf Ave, Staten Island, NY 10314
- #SYR1 – 7211 Morgan Rd, Liverpool, NY 13090
- #BUF5– 4201 Walden Ave, Lancaster, NY 14086
North Carolina
- #CLT4 – 8000 Tuckaseegee Rd, Charlotte, NC 28214
- #GSO1 – 1656 Snow Bridge Ln, Kernersville, NC 27284
- #CLT9 – 3620 Reeves Ridge Dr, Charlotte, NC 28214
- #CTL5 – 1745 Derita Rd, Concord, NC 28027
- #CLT3 – 6500 Davidson Hwy 2532, Concord, NC 28027
- #RDU1 – 4851 Jones Sausage Rd, Garner, NC 27529
- #RDU5 – 1805 TW Alexander Dr, Durham, NC 27703
Ohio
- #CLE2 – 21500 Emery Rd, North Randall, OH 44128
- #AKC1 – 2450 Romig Rd, Akron, OH 44320
- #CMH4 – 1550 W Main St, West Jefferson, OH 43162
- #CMH1 – 11903 National Rd SW, Etna, OH 43062
- #CLE5 – 8685 Independence Pkwy, Twinsburg, OH 44087
- #POH1 – 3880 Groveport Rd, Obetz, OH 43207
- #CMH3 – 700 Gateway Blvd, Monroe, OH 45050
- #CLE3 – 1155 Babbitt Rd, Euclid, OH 44132
- #CMH2 – 6050 Gateway Ct, Obetz, OH 43125
- #CMH6/HCM1 – 3538 TradePort Ct, Building 2, Lockbourne, OH 43137
Oklahoma
- #TUL2 – 11920 E 43rd St N, Tulsa, OK 74116
- #DOK1 – 4401C E Hefner Rd, Oklahoma City, OK 73131
- #OKC1 – 9201 S. Portland Ave, Oklahoma City, OK 73159
- #OKC5 – 1414 S Council Rd, Oklahoma City, OK 73179
Oregon
- #PDX5 – 5647 NE Huffman St, Hillsboro, OR 97124
- #PDX9 – 1250 NW Swigert Way, Troutdale, OR 97060
- #PDX7 – 4775 Depot Ct SE, Salem, OR 97317
- #PDX6/HPD1 – 15000 N Lombard St, Multnomah, Portland, OR 97203
Pennsylvania
- #XUSC – 40 Logistics Dr, Carlisle, PA 17013
- #ABE4 – 1610 Van Buren Rd, Easton, PA 18045
- #PIT2 – 1200 Westport Rd, Imperial, PA 15126
- #AVP8 – 250 Enterprise Way, Pittston, PA 18640
- #ABE1/ABE2 – 705 Boulder Dr, Breinigsville, PA 18031
- #MDT1 – 2 Ames Dr, Carlisle, PA 17015
- #PHL6 – 675 Allen Rd, Carlisle, PA 17015
- #AVP2/AVP3 – 298 1st Ave, Gouldsboro, PA 18424
- #ABE5 – 6455 Allentown Blvd, Harrisburg, PA 17112
- #PHL5 – 500 McCarthy Dr, Lewisberry, PA 17339
- #PIT5 – 2250 Roswell Dr, Pittsburgh, PA 15205
- #AVP6 – 1 Commerce Rd, Pittston, PA 18640
- #DPP1 – 501 North Dr, Sewickley, PA 15143
- #ABE3 – 650 Boulder Dr, Breinigsville, PA 18031
- #PPA1 – 545 Oak Hill Rd, Mountaintop, PA 18707
- #PHL4 – 21 Roadway Dr, Carlisle, PA 17015
- #AVP1 – 550 Oak Ridge Rd, Hazleton, PA 18202
South Carolina
- #CAE1 – 4400 12th St Extension, West Columbia, SC 29172
- #GSP1 – 402 John Dodd Rd, Spartanburg, SC 29303
Tennessee
- #DNA1 – 2813 Brick Church Pike, Nashville, TN 37207
- #STN1 – 10 Dell Pkwy, Nashville, TN 37217
- #BNA2 – 500 Duke Dr, Lebanon, TN 37090 – Wilson County
- #BNA1 – 14840 Central Pike, Lebanon, TN 37090 – Wilson County
- #CHA1 – 7200 Discovery Dr Chattanooga, TN 37421 – Hamilton County
- #MEM5 – 5155 Citation Dr, Memphis, TN 38118
- #BNA5 – 50 Airways Blvd, Nashville, TN 37217
- #CHA2 – 225 Infinity Dr NW, Charleston, TN 37310 – Bradley County
- #BNA3 – 2020 Joe B Jackson Pkwy, Murfreesboro, TN 37127
Texas
- #FTW6 – 2601 W Bethel Rd, Grapevine (Coppell), TX 75261
- #SAT1 – 6000 Enterprise Ave, Schertz, TX 78154
- #XUSB – 14900 Frye Rd, Fort Worth, TX 76155
- #HOU3 – 31819 Highway Blvd, Katy, TX 77493
- #STX2 – 1625 Hutton Dr, Carrollton, TX 75006
- #DAL2 – 2601 S Airfield Dr, Irving, TX 75038
- #DAL3 – 1301 Chalk Hill Rd, Dallas, TX 75211
- #FTW3/FTW4 – 15201 Heritage Pkwy, Fort Worth, TX 76177
- #FTW7/FTW9 – 944 W. Sandy Lake Rd, Coppell, TX 75019
- #DDA8 – 8901 Forney Rd, Dallas, TX 75227
- #DFW1 & DFW8 – 2700 Regent Blvd, Dallas, TX 75261
- #FTW8 – 3351 Balmorhea Dr. Dallas, TX 75241
- #IAH1 – 9155 Southlink Dr, Dallas, TX 75241
- #DFW7 – 700 Westport Pkwy, Fort Worth, TX 76177
- #DDA2 – 3838 W Miller Rd, Garland, TX 75041
- #HOU2 – 10550 Ella St, Houston, TX 77038
- #PTX1 – 2101 Danieldale Rd, Lancaster, TX 75134
- #DAL9 – 1400 Southport Pkwy, Wilmer, TX 75172
- #DFW6 – 940 W Bethel Rd Coppell, TX 75019
- #SAT2 – 1401 E McCarty Ln, San Marcos, TX 78666
- #FTW2/HDA1 – 2701 W Bethel Rd, Coppell, TX
Utah
- #SLC4 – 770 South Gladiola, Suite 500, Salt Lake City, UT 84104
- #SLC2 – 6802 W Old Bingham Hwy, West Jordan, UT 84081
- #SLC1 – 777 N 5600 W, Salt Lake City, UT 8411
- #SLC3/HSL1 – 355 N John Glenn Rd, Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Virginia
- #DDC4 – 44301 Mercure Cir, Sterling, VA 20166
- #KRB2 – 7000 Hardware Dr, Prince George, VA 23875
- #RIC5 – 11600 N Lakeridge Pkwy, Ashland, VA 23005
- #BWI4 – 165 Business Blvd, Clear Brook, VA 22624
- #RIC3/#HRC1 – 4949 Commerce Rd, Richmond, VA 23234
- #BWI1 – 45121 Global Plaza, Sterling, VA 20166
- #RIC2 – 1901 Meadowville Technology Pkwy Chester, VA 23836
- #HDC1 – 6885 Commercial Dr, Springfield, VA 22151
- #RIC1 – 5000 Commerce Way, Petersburg, VA 23803
Washington
- #BFI1 – 1800 140th Ave E, Sumner, WA 98390
- #SEA6/#SEA8 – 1227 124th Ave, Northeast Bellevue, WA, 98005
- #BFI5 – 20526 59th Pl S, Kent, WA 98032
- #GEG1 – 10010 W Geiger Blvd, Spokane, WA 99224
- #DSE4 – 6611 Associated Blvd, Everett, WA 98203
- #BFI7 – 1901 140th Ave E, Sumner, WA 98390
- #BFI3 – 2700 Center Dr, Dupont, WA 98327
- #BFI6 – 20202 84th Ave S, Kent, WA 98032
- #BFI8 – 20529 24th Ave S, SeaTac, WA 98198
- #DES7 – Sumner, WA 98390
- #BFI4 – 21005 64th St, Kent, WA 98032
- #PWA1 – 2309 Milwaukee Way, Tacoma, WA 98421
Wisconsin
- #MKE2 – 9700 South 13th St, Oak Creek, Wisconsin 53154 – Milwaukee County
- #MKE1 – 3501 120th Ave. Kenosha, WI, 53144
- #DML1 – 3935 W Mitchell St, Milwaukee, WI 53215
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an Amazon sort center and a fulfillment center?
Amazon fulfillment centers are responsible for filling customer orders. They receive orders, pick items, pack them up, and prepare them for shipping. On the other hand, Amazon sort centers aggregate shipments from other Amazon facilities and sort them based on zip codes to prepare them for delivery.
Where is Amazon’s largest fulfillment center?
Amazon’s largest fulfillment center is currently under construction in Ontario, California, and is slated to cover 4.1 million square feet.
How many Amazon fulfillment centers are there?
Amazon currently operates over 175 fulfillment centers globally.
Does Amazon have its own fulfillment centers?
Yes, Amazon owns and operates hundreds of fulfillment centers all over the world.
How big are Amazon fulfillment centers?
Amazon fulfillment centers vary by size depending on the location but are typically between 600,000 and 1 million square feet.