Influencer Marketing Hub sets itself apart from conventional review platforms through the involvement of eCommerce experts such as Werner Geyser, Djanan Kasumovic, Camille Kennedy, Dave Eagle, and other notable industry figures. This expert team brings a profound understanding of the eCommerce landscape, assessing tools and platforms with an insider’s perspective on capabilities, experience, and industry acumen. Unlike user-generated review platforms, Influencer Marketing Hub’s evaluations are rooted in extensive firsthand experience and direct interactions with the tools and platforms in question. This ensures that the reviews are not only trustworthy but also deeply informed. High-caliber brands like Sellozo, Disruptive Advertising, and Sociallyin undergo rigorous monthly evaluations, highlighting the platform’s commitment to identifying and showcasing top-tier solutions in eCommerce and beyond.
Influencer Marketing Hub has consistently been recognized by leading media outlets for our authoritative data, findings, and insights within the eCommerce landscape. Our platform is frequently cited as a trusted source of information, demonstrating the value and impact of our work in shaping industry standards and practices.
Influencer Marketing Hub employs an expert-driven methodology to evaluate eCommerce agencies, ensuring that our recommendations are both reliable and comprehensive. This approach is designed to help businesses and individuals find the best agencies to meet their specific eCommerce needs. Here’s how we assess the various agencies like Sellozo, Disruptive Advertising, and Sociallyin:
When you're strategizing how to scale your brand or boost sales through your online store, it's easy to overlook just how vast and competitive the eCommerce sector has become. Over the years, the industry has become massive enough to account for 19% of all retail sales worldwide. That roughly translates to $6.4 trillion in sales, projected to increase to $7 trillion by 2025.
Becoming a part of this sector requires a ton of prior groundwork that only grows more complicated every day. It's no longer enough to have a website and a payment portal; you need to be on top of your marketing game, too. eCommerce marketing agencies can help in this regard.
Consider them your right-hand partners, as they tackle everything from SEO optimization to paid campaigns. eCommerce marketing agencies come with sufficient expertise and knowledge to take your business from a tiny shop on the web to a full-fledged brand. Here's a round-up of some of the best agencies to work with.
Top eCommerce Marketing Agencies to Elevate Your Brand:
1. Sellozo

Location: Vancouver, WA
Industries: eCommerce
Pricing: Offers flat-fee pricing; specific rates available upon request
Sellozo distinguishes itself in eCommerce marketing by providing specialized Amazon PPC management services. What distinguishes them is their unique blend of AI-driven technology and expert human strategy. Their US-based team of Amazon eCommerce experts is adept at crafting and executing advertising strategies that drive substantial business growth.
Key eCommerce marketing services offered by Sellozo include strategy development, comprehensive campaign setup, and advanced keyword discovery. They excel in maximizing campaign performance, focusing on reducing wasted ad spend and enhancing return on investment.
But that’s not it. Sellozo doesn’t only enter the picture when it comes to marketing your readily-built online store. They can assist you even before that with services like content and campaign strategy, product and brand videos, product and lifestyle photography, SEO-forward copywriting, and graphic design. So, Sellozo starts by setting up a well-optimized eCommerce store for you and then goes on to manage your marketing and advertising campaigns.
One of the main benefits of partnering with Sellozo is its strong penetration in the eCommerce market. For example, when Walmart added API partners to Walmart Connect’s retail media network, Sellozo was one of the few chosen ones. Sellozo joined CommerceIQ, the eCommerce management solution Walmart partnered with to provide its clients with a thorough understanding of Walmart’s digital shelf and to help them optimize their presence on the retail giant’s platform.
Similarly, Voltage, a top digital marketing services provider for Amazon’s private label space, also joined hands with Sellozo, resulting in a 100% increase in revenue in just 14 days for multiple businesses.
Sellozo in Numbers
Part of the reason Sellozo is just a sought-after eCommerce marketing agency is its impressive performance metrics and numbers. Here’s a glimpse:
- Driving $2 billion+ in annual sales
- Automating 12 million ads
- Spending $245 million annually on client campaigns
As you can see, the ROI of $2 billion on a meager spend of $245 million shows how efficient their campaigns are in generating sales. Sellozo’s human-AI campaign management is the backbone of this efficiency.
Sellozo’s Technology: Campaign Studio
Sellozo’s Campaign Studio is a proprietary platform with simple drag-and-drop functionality that allows you to visualize your eCommerce strategies in one place. You can use it to:
- Harvest keywords for ad campaigns
- Create custom campaign flows
- Test exact, phrase, and broad match keywords for eCommerce PPC campaigns
- Replicate existing campaigns to amplify results
Plus, Sellozo’s AI dayparting tool uses hourly advertising cost of sale (ACoS) data to automate your eCommerce ad campaigns. It helps maximize ROI by showing your ads during peak sales windows. You also get heat map data insights and hourly trends to refine your eCommerce advertising strategies.
Sellozo Success Story
The way Sellozo approaches marketing for eCommerce clients is evident in their campaign for Commercial Canal, a distribution and licensing agency in New York City. Commercial Canal wanted to streamline eCommerce advertising for its clients, and Sellozo proved to be the ultimate solution.
Sellozo success story
Strategic Approach
Here’s how Sellozo helped the client reach their goals:
- Automatically discovered keywords for Amazon ad campaigns
- Made quick changes to keywords and campaigns for real-time optimization
- Used AI to adjust daily budgets and bids
- Uses dayparting to optimize campaigns for hourly and daily performance
- Mapped client’s strategies using custom templates
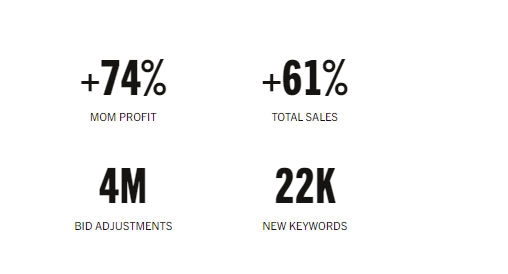
Resulting in bid adjustments of $4 million and a 61% increase in total sales, the campaign was a major success.
They specialize in:
- Amazon Advertising Optimization
- Increasing Ad Profit
- Dayparting Strategy Implementation
2. Disruptive Advertising

Location: Pleasant Grove, UT
Industries: B2B, eCommerce, education, legal
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
Disruptive Advertising is one of those eCommerce agencies that have been in business so long that they are profiled by industry publications, like Research Nester digital marketing reports, as benchmarks for the marketing agency sector as a whole. The agency’s difference lies in its selection of clients.
They don’t just work with anyone. Instead, they conduct a free audit for clients that approach them and then decide if the client is a good fit for their services. Their eCommerce services include SEO, Amazon management, paid search, automated nurturing, and website CRO.
When required, they also provide email marketing and creative services to drive sales for their eCommerce clients.
Even better, Disruptive is always on top of new marketing trends, which they incorporate seamlessly into their clients’ strategies. For example, they were a partner for the Google Summit, which focused on search engine ad analytics and AI innovations, marketing insights, and paid media trends.
As Google’s Top Premier Partners, the agency is able to bring some of its clients to the search engine giant’s headquarters for exclusive insights right from the source. This level of commitment and collaboration with their clients is what sets Disruptive Advertising apart from others in the market.
The agency has previously participated in The Global Ecommerce Acceleration Summit, where they gained fresh insights from the world of eCommerce to apply to their clients’ strategies.
Besides B2C, Disruptive Advertising also provides eCommerce marketing services to B2B clients. Considering that Amazon Business’s sales reached $75.2 billion in 2023, the B2B eCommerce segment is huge, and businesses in this sector can get specialized assistance from Disruptive for CRO, eCommerce advertising, and more.
With the agency ranking #8 out of 280,000 contenders on Clutch’s list of the top B2B service providers, selecting it as your partner is a wise choice.
The Disruptive Advertising Solution
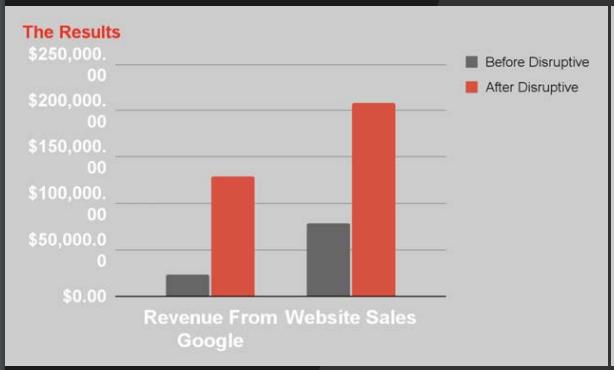
When Bunny James, a food eCommerce brand, came to Disruptive, they were already doing well on Amazon but had trouble replicating these results on their website. Disruptive realized that their website needed a lot of work, and the eCommerce campaign had to be optimized.
Bunny James case study
Strategic Approach
Here’s how Disruptive Advertising steered the client’s eCommerce strategy:
- Optimized the client’s shopping feed
- Added new product titles with high-volume keywords
- Restructured the search campaign
- Tested keyword variations to find the words that would deliver the best results
- Tested multiple variations of the ad copy
- A/B tested landing pages
Bunny James not only got 25,000 new users but also saw a 2x return on ad spend as a result of this campaign. Disruptive also ran an email marketing campaign for the client, which resulted in a 530% increase in sign-ups and a 393% year-over-year increase in revenue.
Their services include:
- Paid search
- Paid social
- Email marketing
- Website optimization
- Creative strategy
- Landing page design and testing
3. Sociallyin

Locations: Atlanta, GA (headquarters); Birmingham, AL; Frisco, TX
Industries: Automotive, communication, construction
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
If you want to make social media one of your focus areas, be sure to turn to Sociallyin. They create result-driven strategies for brands to help them with various social media marketing activities. Their team of social media marketing consultants, creatives, and strategists are up to date with the latest tactics and trends to help you create fresh campaigns.
Hiring a professional agency like Sociallyin to manage your eCommerce SEO is an invaluable asset when it comes to scaling your online store. Specialized teams of experts have the knowledge, experience, and resources to turn your website into a competitive force in the digital space.
From crafting effective web design strategies to optimizing on-site content, they can ensure that your website has what it takes to draw in targeted customers and maximize ROI.
Their specialties include:
- Brand awareness
- Paid advertising
- Social media community management
- Analysis and reporting
4. WEBITMD

Locations: Los Angeles, CA; Miami, FL
Industry: eCommerce, business, consumer products and services, hospitality and leisure, manufacturing
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
WEBITMD, a proficient digital marketing agency, has made a name for itself as the one-stop solution for businesses aiming for eCommerce growth.
Their services, devised by direct-to-consumer experts, deliver comprehensive and data-driven solutions to effectively elevate your eCommerce store. Over 250 eCommerce brands have entrusted their growth to WEBITMD, a testament to their deep understanding of the direct-to-consumer market. Leveraging this knowledge, they’re able to boost sales and maximize your Return on Ad Spend (ROAS).
At WEBITMD, the process is exhaustive and meticulous. It starts with a profound understanding of your business model, extending to competitor analysis, campaign diagnostics, and goal setting. They design high-performance campaigns that they optimize continuously, focusing on key areas such as Paid Search & Social, Shopping Ads, eCommerce Marketplaces, and Remarketing & Display.
The agency also provides ongoing guidance to existing and potential clients. Their Commerce Marketing Playbook is filled with strategies and examples to help businesses develop their eCommerce marketing plans.
Discover #eCommerce marketing best practices across multiple channels to stay ahead of the curve in our new #eBook.
The WEBITMD eCommerce #Marketing Playbook https://t.co/YiwAtY48KN
— WEBITMD – A Digital Growth Agency (@webitmd) March 28, 2024
WEBITMD’s eCommerce PPC offering is their top service due to the agency’s understanding of Facebook Ads, YouTube Ads, Microsoft Advertising, Google Ads, Amazon Ads, and other major platforms.
However, PPC isn’t the only aspect in which WEBITMD’s expertise shines. The agency offers a full-fledged eCommerce plan to its clients, which includes messaging and positioning, design and visual identity, email marketing, marketing automation, content marketing, and website development.
WEBITMD HubSpot Onboarding
Besides DTC eCommerce marketing, WEBITMD also specializes in HubSpot onboarding. The agency can sync your BigCommerce or Shopify eCommerce store with HubSpot to give you these additional features:
- Customer Segmentation: With shopper data in the HubSpot CRM, you can use a variety of customer segmentation tools.
- Marketing Automation: This integration also lets you automate eCommerce marketing activities like cart abandonment recovery and re-engagement workflows.
- Direct Attribution Reporting: With this feature, you get direct insight into where you’re earning your revenue from, be it Facebook ads, Google ads, or any other marketing channel.
WEBITMD Growth Stack
For established eCommerce businesses that want to grow, WEBITMD offers its Growth Stack. It’s a revenue-generating service that includes a host of eCommerce marketing services like CRM onboarding, messaging and positioning, sales operation, marketing automation, revenue operations, and paid media.
It also comes with a reporting dashboard where you can track data related to your eCommerce marketing campaigns and see how they are contributing to your revenue growth.
The WEBITMD Solution
Despite its considerable scale, WEBITMD doesn’t only provide eCommerce marketing services to large businesses. The agency has helped new businesses like Andys’ Hay achieve a 118% increase in conversion rates, too.
Before coming to WEBITMD, Andy’s Hay had already spent $50k in PPC advertising for their eCommerce store, but to no avail. Things turned around when WEBITMD got involved.
Any new business faces a major challenge in its early stages: finding an audience and carving out a place in its industry. After implementing our paid strategy, Andy’s Hay ads and content reached 2.3 million people and saw a 5x boost in ROAS on Amazon. https://t.co/7UvFwodjqs
— WEBITMD – A Digital Growth Agency (@webitmd) December 19, 2023
Strategic Approach
- Here’s how WEBITMD helped the client kickstart their eCommerce business:
- Optimized the client’s Amazon and Google ads to maximize conversions
- Optimized top-of-the-funnel blog content to boost lead generation
- Set ROAS targets to only increase ad budget if it would be profitable
- Implemented a multi-channel paid social strategy
The client did not only see a 280% increase in online orders but also got a 500% ROAS.
They specialize in:
- Competitor Analysis
- Social
- Shopping ads
- eCommerce marketplaces
- Content marketing
- Email marketing
5. Nuanced Media

Locations: Tucson and Phoenix, AZ
Industries: eCommerce, manufacturing, retail
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
Nuanced Media is a full-service eCommerce and Amazon marketing services agency. They describe themselves as “Brand Champions,” and instead of limiting their services to certain industries, they choose to work with businesses that show strong leadership and communication skills as well as opportunities for growth.
Using the latest eCommerce marketing strategies, like affiliate marketing, and/or more traditional strategies, such as search engine optimization, will help ensure you unlock these growth opportunities.
When Nuanced Media takes over eCommerce marketing for you, they leave no stone unturned. They manage your eCommerce campaigns from start to finish with services like influencer marketing, wholesale and retail consulting, affiliate marketing, website design, media buying, and social media promotions.
If you’re planning to sell in an eCommerce marketplace, Nuanced Media also provides marketplace setup and optimization services. They also offer fulfillment and inventory management to streamline order management. From CRO optimization to retargeting and cart abandonment recovery, the agency does it all.
For clients particularly interested in Amazon eCommerce, Nuanced Media offers PPC ad management for sponsored brand ads, product display ads, DSP ads, and more. They also make adjustments to your Amazon campaigns based on A/B testing and detailed analytics.
With the expertise of Patrick Hanna, the agency’s eCommerce marketing strategist who has previously worked at Amazon, Nuanced Media has insider knowledge on making its clients’ eCommerce businesses a success.
The agency’s experts also share this knowledge with others through industry events, conferences, and podcasts, indicating their thought leadership. For example, the agency’s CEO Ryan Flannagan was invited on the eCommerce Odyssey podcast to talk about growing an eCommerce business on Shopify, Amazon, Google, and eBay.
The Nuanced Media Solution
Nuanced Media has helped its fair share of clients grow their eCommerce businesses, especially on Amazon. One such client is Manna Supplements, a newbie trying to make its name in the competitive supplement industry.
Their key challenge was that they were new and struggled with click-through rates. They were solely relying on sponsored product ads for advertising and had a narrow PPC campaign focus. Due to these limitations, they were unable to drive the results they should have from their eCommerce strategy.
Nuanced Media stepped in to make their store more visually appealing and use a blend of Amazon advertisements to boost brand visibility.
Manna Supplements case study results
Strategic Approach
Nuanced Media took the following steps to address Manna Supplements’ challenges and drive growth:
- Conducted A/B testing to optimize product images for the client’s online store
- Diversified advertising channels on Amazon
- Expanded the existing PPC campaigns by including high-volume non-branded keywords in addition to branded keywords
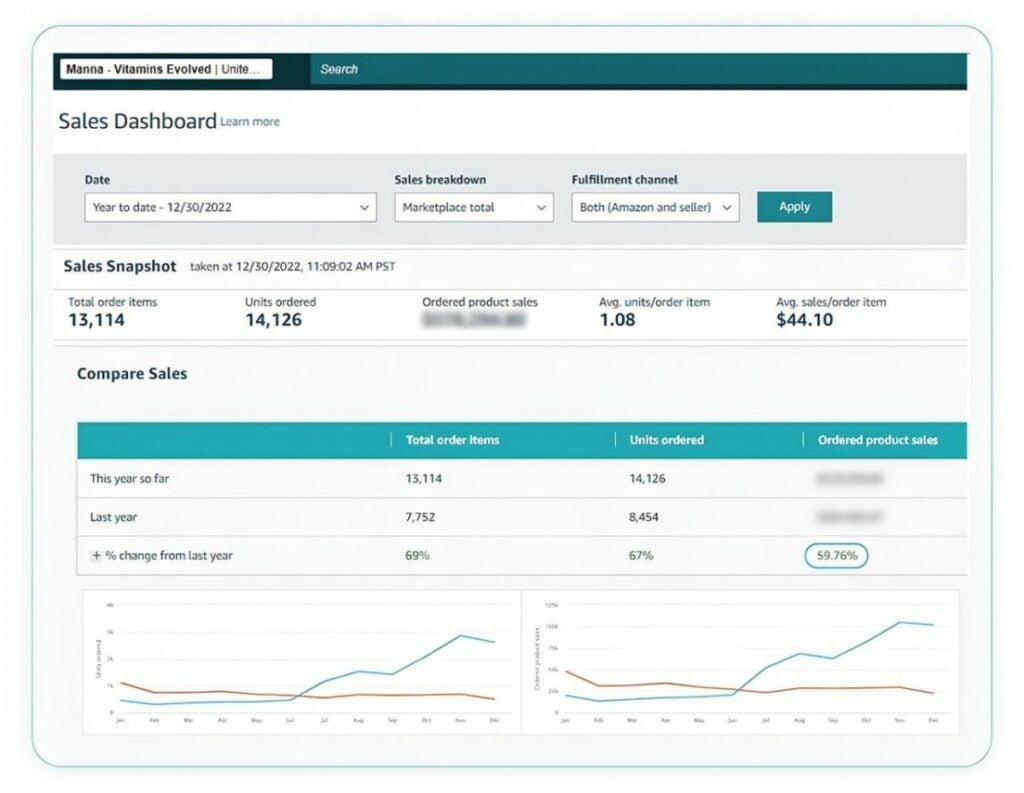
These tactics helped the client rank at #17 in the Curcumin Herbal Supplement category. They also experienced a 59.76% increase in gross revenue in just six months.
Their specialties include:
- Website design and optimization
- SEO
- Email marketing
- Forecasting and projections
- Branding
6. SmartSites

Location: Paramus, NJ
Industries: Medical and healthcare, legal, automotive, retail, B2B, hospitality, non-profit
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
Launched a decade ago by two brothers sharing a love for all things digital, SmartSites has assisted countless clients from all over the world to get more organic traffic for their eCommerce sites.
Boasting a remarkable 97% rating from their customers on the quality of their services, their hard work has been recognized by multiple bodies, including an A+ rating from the Better Business Bureau and a citation as one of the “Best Entrepreneurial Companies in America” by Entrepreneur magazine.
To date, they have helped their clients generate more than $100 million in revenue. With regards to eCommerce website development specifically, they can work with eCommerce sites on a wide range of platforms, including Magento, WooCommerce, Shopify, PrestaShop, and BigCommerce.
While the agency specializes in all major online marketplaces, its Shopify expertise is matchless. They are always on top of whatever is new in the Shopify world, be it integrating apps or updating plugins. Plus, they host events in collaboration with Shopify to get first-hand experience with the latest features and development changes.
SmartSites is also a Shopify Partner, which means they are the first to receive training and support from Shopify to ensure that their client’s websites are optimized for success on the platform. The agency also has a Shopify Masterclass, where you can learn how to acquire, convert, and retain eCommerce customers.
In addition to offering top integrated eCommerce marketing solutions, they are also one of the best SEO agencies to help you with long-term success. The agency enhances the SEO for your eCommerce website to ensure higher visibility and drive more traffic to your online store.
They also couple their SEO strategies with email marketing to bring in new customers and increase repeat purchases. Their partnership with Mailchimp allows them to provide direct-from-the-source updates to their clients’ email marketing strategy.
Plus, their Director of Email Marketing, Ashley Ismailovski, is also the co-leader of Klaviyo Community’s New York City chapter, which means she can further bring more professional insight to the clients’ eCommerce email marketing strategies.
Furthermore, SmartSites provides pay-per-click (PPC) advertising services to complement their eCommerce marketing and SEO solutions. This includes Google Ads, Facebook Ads, eCommerce platform ads, remarketing strategies, and more.
SmartSites Partnerships
SmartSites has partnered with some of the top eCommerce tools to bring their functionality to its clients. For example, they are a Refersion partner, bringing the tools of affiliate marketing to their clients.
They also partner with Be Pantastic to leverage their tool, UpOrder, a repeat purchase enhancement feature for Shopify. The branded email templates and product recommendations offered by this tool increase post-purchase sales for SmartSites’ clients.
SmartSites has also got Recart, an eCommerce messenger marketing tool, on board to help retailers recover abandoned carts and increase overall sales.
As for eCommerce website enhancement, the agency partners with Termly to ensure its clients’ websites are legally compliant and user-friendly. Together, these partnerships allow SmartSites to provide comprehensive marketing solutions for eCommerce businesses.
The SmartSites Solution
SmartSites revealed its expertise in the campaign it ran for Forever Lux, a discounted fragrance store. Since the client was in a super-competitive market, where large names already dominated, they had trouble ranking for keywords relevant to their industry. SmartSites stepped in to provide a solution.
SmartSites case study
Strategic Approach
Here’s what SmartSites did for Forever Lux:
- Implemented a site-wide optimization strategy to improve rankings for all pages
- Created a blog to increase organic traffic
- Launched a link-building campaign
- Developed a Mailchimp template for customer interaction automation
- Created Product List Ads to acquire new customers
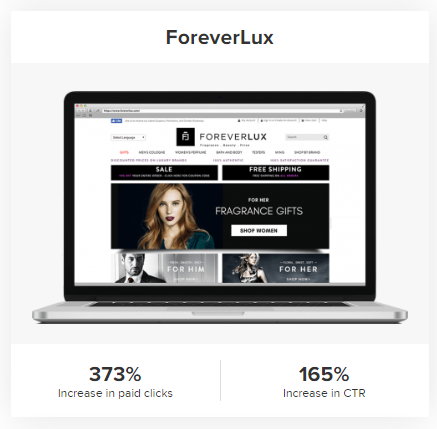
The results were nothing short of remarkable, with a 373% increase in paid clicks and a 165% increase in click-through rate on the client’s website.
Their services include:
- PPC
- SEO
- Web design
7. NinjaPromo

Locations: London, UK; Dubai, UAE; Singapore; Hong Kong; New York, NY
Industries: B2B, fintech, SaaS, startups, small business, gaming, esports, mobile, cryptocurrency
Pricing: $50-$99 average hourly rate
NinjaPromo can handle basically all services related to digital marketing like a ninja. Their team of marketing ninjas can create a powerful marketing strategy for your online store. They believe that creating a solid foundation is key and will create a detailed roadmap to steer you on your path to consistent growth.
To them, it’s a long journey, not a short-distance dash. They extend their scope to beyond merely the basics and use A/B testing, among other things, to yield maximum results.
From optimizing your store to designing ads to creating content that converts, they can help you with various services. Plus, if you want to expand your focus to Amazon, they can assist you in reaching a new group of online shoppers.
Their specialties include:
- eCommerce SEO
- eCommerce PPC
- Social media marketing
- Content marketing
8. Moburst

Locations: New York, NY; San Francisco, CA; Tel Aviv, Israel; London, UK
Industries: Arts and entertainment, consumer products and services, media, supply chain and logistics, transport, utilities, eCommerce
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
Founded in 2013, Moburst is one of the top full-service, digital agencies. Trusted and loved by well-known brands like Samsung and Uber, they can help with consulting and marketing. With regards to their marketing services specifically, their team can help you with everything from crafting a high-impact strategy to social media management, and everything in between.
They offer an all-in-one package to help you strike the right balance between organic and paid social media. To ensure that they’re on the correct path, each month they will also investigate what delivered results. This includes identifying the optimal time to post, post frequency, and which type of content to create.
Their specialties include:
- Brand positioning
- Copywriting
- SEO
- Localizations
- Email marketing
- Website development
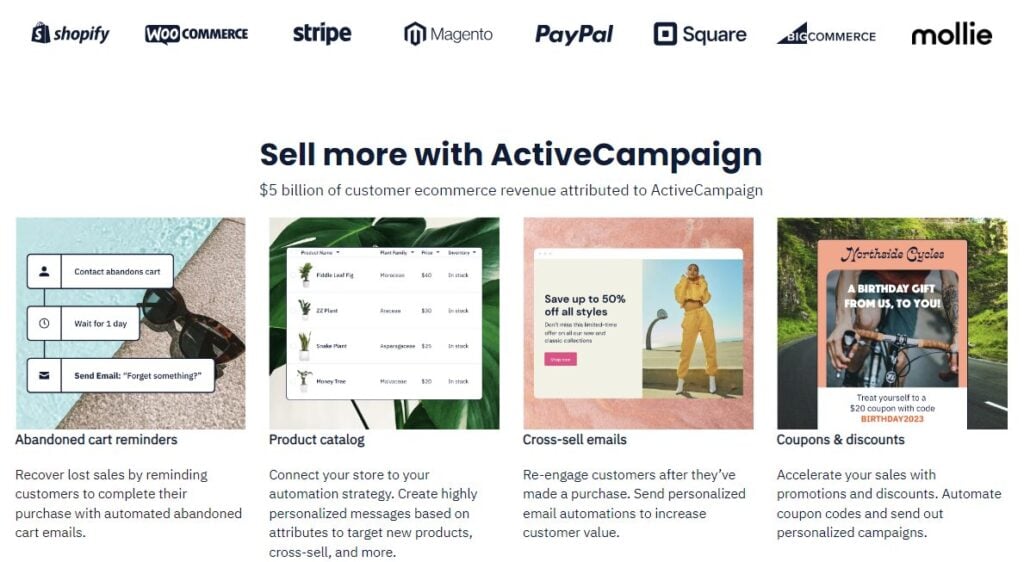
9. ActiveCampaign

Location: Chicago, IL
Industries: eCommerce, SMB, enterprise, healthcare, education, nonprofit, consulting
Pricing: Entry point for eCommerce is $8/month (first 3 months, then $15).
ActiveCampaign for eCommerce helps boost your online sales, attract more customers, cultivate brand ambassadors, and save time. The company automates revenue-driving activities using marketing automation and personalization tools to grow your online store.
It helps you reach and engage customers beyond the initial sale to increase brand loyalty. It enables you to seamlessly connect to your customers across all channels – email, SMS, and social media. Furthermore, it lets you drive repeat sales with customization and timely communications.
One exceptional feature of ActiveCampaign for eCommerce is its automation capabilities. Through AI-powered CRM, you gain access to intelligent marketing tools that enhance your customer journeys, ultimately boosting sales. Automation features encompass:
- abandoned cart recovery,
- personalized product recommendations,
- site tracking,
- mapping customer journeys,
- order and event follow-ups,
- behavior-based segmentation,
- built-in CRM,
- real-time insights, and more.
Automating tailored product recommendations means a tailored shopping experience. You can leverage store and behavior data to present customers with the products or services that resonate with their unique preferences. In addition to boosting average order values, personalized recommendations cultivate stronger connections and fortify long-term customer value.
ActiveCampaign for eCommerce enables you to optimize your product catalog. You can sync all your products into the platform and create highly personalized messaging for each customer based on data attributes. This way, you can promote new products, cross-sell complementing items, and unlock repeat purchases. An automated product catalog helps you build targeted campaigns using dynamic filters, A/B testing, personalization tags, and conditional content.
Another standout feature of ActiveCampaign for eCommerce is its extensive channel management tools. The powerful platform can tailor emails and SMS, empowering your business to connect beyond your target audience.
This feature includes a user-friendly drag-and-drop email designer, ready-made templates, inbox preview, content manager, AI-powered email content generation, predictive sending, site messaging, deliverability enhancements, and more.
Its comprehensive communication channels generate transactional emails for order updates, enable instant customer engagement via SMS, create landing pages for campaign conversions, and facilitate precise audience targeting for ads.
ActiveCampaign for eCommerce also features detailed store and customer insights. This real-time information and activities across all touchpoints can help you better understand your customers.
These insights include store and campaign performance metrics, conversion rates, revenue attribution, customer purchase history, data visualization, customer segmentation, and cross-channel analysis.
Among the best attributes of ActiveCampaign for eCommerce is its top-tier integrations and API. With the most diverse third-party app ecosystem, ActiveCampaign syncs and automates data from eCommerce platforms and tools you use to make your day-to-day operations run smoothly.
The company integrates your online store for real-time synching with eCommerce powerhouses, such as Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, Magento, PayPal, Square, and Stripe. Using the platform’s built-in CRM, you will have all your customer data in one place, which makes automating, tracking, and measuring every customer interaction effortless and widespread.
ActiveCampaign for eCommerce automates everything for all types of businesses. You can run an omnichannel marketing strategy for all your stores – online or physical. You can connect with your audiences using the proper channels at the best times when they’re likely to engage. You can keep track of all interactions to trigger automation that customizes the customer’s unique experience.
A good example is ActiveCampaign’s partnership with Party Headphones. This eCommerce rental store specializing in entertainment equipment teamed up with ActiveCampaign to help track, measure, and optimize conversion rates using traffic, keywords, and campaigns.
ActiveCampaign’s conversion services provided CRM capabilities to engage with prospects and existing customers at a moment’s notice. Using ActiveCampaign for eCommerce also helps Party Headphones integrate with WooCommerce, Nectar Desk, and Zapier seamlessly. The campaign yielded a 480% increase in contacts and three times faster client intake.
10. Thrive Internet Marketing Agency

Locations: Dallas, TX (headquarters); Atlanta, GA; Arlington/Austin/Houston/San Antonio, TX; Baltimore, MD; Chicago, IL; Cleveland, OH; Denver, CO; Jacksonville/Miami/Orlando FL; Kansas City, MO; Las Vegas, NV; Los Angeles/San Diego, CA; Louisville, KY; Manhattan, NY; Minneapolis, MN; Myrtle Beach, SC; New Orleans, LA; Philadelphia, PA; Portland, OR; Seattle, WA
Industries: Education and finance, health and medical, home services, manufacturing
Pricing: $100-149 average hourly rate
Thrive Internet Marketing Agency is an established and respected marketing agency that offers a long list of marketing-related services, including eCommerce marketing. They understand the demands and challenges that online businesses face and to help ensure their clients’ success they implement cross-channel strategies and tried-and-tested optimization methods.
The results that they’ve achieved for their clients are testament to their expertise. For example, they helped one eCommerce store to generate more than $170,000 in revenue and a return on advertising spend of over 2,000% in just two months.
Their specialties include:
- SEO and PPC
- Content marketing
- Website design
- Amazon marketing
- Social media marketing
11. 1Digital Agency

Locations: Hollywood, FL (headquarters); Philadelphia, PA
Industries: eCommerce, consumer products and services, fashion, alcohol and tobacco, automotive, medical
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
Founded in 2012, 1Digital Agency describes themselves as an eCommerce growth agency. Their team of more than 50 in-house experts has helped their clients to build hundreds of eCommerce websites across various industries.
As one of the preferred partners of Shopify Plus, BigCommerce, Magento, and Volusion, they are one of the top choices if you want to use one of these eCommerce platforms specifically. In fact, Neil Patel has voted them as the best eCommerce agency for BigCommerce customization.
Their specialties include:
- Marketing
- Support
- SEO and PPC
12. Absolute Web

Locations: Miami, FL (headquarters); Los Angeles, CA; Lisbon, Portugal
Industries: eCommerce, retail, consumer products and services, manufacturing
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
Founded in 1999, Absolute Web has been in the business for more than two decades! While they are a full-service agency, they have strong skills in eCommerce development and management specifically, making them one of the top eCommerce agencies to grow and market your brand.
As strategic partners of BigCommerce, Magento, and Shopify, their team of developers, designers, trend forecasters, and digital strategists specifically specialize in custom development of eCommerce solutions for these platforms.
With a six-year streak as part of the renowned Inc. 5000 list in 2023 and Searchspring’s Magento Partner of the Year in 2022, it is no wonder that brands like Beverly Hills Polo Club and Blackbird Cigar have used them for their eCommerce projects.
Their services include:
- Branding
- Digital marketing
- Content production
- UI/UX design
13. Avex Designs

Location: New York, NY
Industries: Consumer products and services, eCommerce, retail
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
If you have a fashion or lifestyle brand and you specifically need help with email marketing, Avex Designs is one of the top email marketing agencies to help you grow your brand. Avex uses a data-backed approach to help with UX design services, conversion rate optimization, and eCommerce development. As a Shopify Plus Partner Agency, they mainly focus on optimizing and marketing websites built with Shopify.
Their services include:
- UX design and development
- Klaviyo email marketing
- Branding
- eCommerce discovery
14. DigitlHaus

Location: Miramar Beach, FL
Industries: Financial services, hospitality and leisure, retail, eCommerce
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
DigitlHaus is an award-winning, full-service eCommerce agency. While their headquarters are in Florida, they pride themselves in the remote agency culture that they have fostered which has allowed them to hire the best talent across the globe.
They work with a wide range of brands that include Fortune 500 companies, the B2B sector as well as B2C brands and have worked with clients like Lowe’s. From automotive to consumer goods, they have served multiple markets.
While not limited to these, their services include:
- Branding
- eCommerce strategy
- Conversion optimization
- SEO
15. Groove

Locations: Baltimore, MD; Philadelphia, PA; Austin, TX; Orlando, FL
Industries: Consumer products, eCommerce, manufacturing, retail
Pricing: Contact them for a custom quote.
Whether you simply need help with your eCommerce website or need more insight into developing an effective eCommerce marketing plan, Groove is a full-service eCommerce agency that can help you to build websites and implement eCommerce marketing best practices.
They were founded in 2007 and have earned awards and recognitions from Inc. 5000 and the US Agency Awards. Brands that they have worked with include Hershey’s, US Open Shop, and Cutter & Buck.
Their services include:
- Website support
- eCommerce SEO
- Email marketing
- eCommerce PPC
16. Inflow

Location: Denver, CO
Industries: Consumer products and services, travel and tourism, health and wellness, beauty and fashion, B2B, custom products
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
Inflow is viewed as one of the best eCommerce marketing agencies by Google, McAfee Security, and Moz. They are also one of the oldest eCommerce companies boasting 14 years of experience in the field. Instead of trying to offer various services, Inflow has decided to focus on search engine optimization (SEO), paid search advertising, and conversion rate optimization and only with eCommerce businesses.
All in all, thanks to their specific focus they are one of the best eCommerce specialists for help with marketing and advertising.
Their services include:
- PPC
- SEO
- Content marketing strategies
- Paid social
17. Kobe Digital

Locations: Los Angeles, CA (headquarters); Miami, FL; New York, NY; Las Vegas, NV; Phoenix, AZ
Industries: Consumer products and services, eCommerce, arts and entertainment, IT, medical
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
Kobe Digital is one of the top agencies if your target audience is mainly millennials. This young, up-and-coming eCommerce agency ensures that they keep up to date with what is currently trending to help their clients engage more effectively with younger users.
Not only can they help you to create eCommerce websites and apps, but they can also help you with branding by identifying your value propositions and unifying your messaging. For example, for Non-stop Watches they created a fully customized website that showcases the values behind the brand and an intuitive product catalog.
Their services include:
- SEO
- Social media marketing
- Custom campaigns
- PPC
18. Lounge Lizard

Locations: New York, NY (headquarters); Long Island, NY; Nashville, TN; Miami, FL; Washington D.C.; Los Angeles, CA; Charleston, SC; Richmond, VA
Industries: eCommerce, consumer products and services, construction, business services, automotive, education, finance, entertainment, medical, media, manufacturing, legal
Pricing: $10,000 minimum project size
Lounge Lizard is one of the top eCommerce agencies that can help you with marketing your online store. With offices across the US, they have helped clients like Blue Foundry Bank, Digital Optometrics, and Festo. From helping you to establish your brand voice to creating a mobile app, they offer a wide range of ROI-driven digital marketing services.
In addition to eCommerce marketing, they can also help you with:
- Branding
- UX/UI
- Interactive design
19. NP Digital

Locations: Las Vegas, NV, with 17 global offices in North America, Australia, Asia, Europe, and South America
Industries: Advertising and marketing, business and financial services, IT, non-profit
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate
Trusted by successful online companies such as Crazy Egg, Hello Bar and KISSmetrics, NP Digital is a performance marketing agency that was created by marketers. With offices across the world, their clients include the likes of Facebook, eBay, and Adobe XD. For example, for Adobe XD they are currently helping to market, optimize, and grow its live site.
Their services include:
- Paid search marketing
- Content marketing
- SEO
- Social media marketing
- Data, analytics and insights
20. RNO1

Locations: San Francisco/Los Angeles, CA; Seattle, WA; Vancouver, Canada; Vilnius, Lithuania
Industries: Business and financial services, media, consumer products and services, arts and entertainment
Pricing: $200-$300 average hourly rate
From crafting eCommerce strategies to implementing UI/UX design, RNO1 offers various services aimed at eCommerce brands. With regards to eCommerce specifically, they strive to create experiences that are purposeful as well as profitable.
One of their eCommerce projects that deserves a mention is the work that they have completed for LOLIWARE, the world’s first edible bioplastics. The deliverables included a digital strategy, creative direction, prototyping, CMS development, and UX/UI design. The project was so successful that LOLIWARE aired on “Shark Tank”, the hit US TV show.
Their services include:
- Branding
- SEO
- Web and app development
- Growth strategy
- PPC
- Email marketing
21. Shero

Location: Red Hook, NY
Industry: eCommerce, business and technology, consumer products and services, non-profit, home and interior décor, industrial and utility
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
If you need help specifically with pay-per-click campaigns, be sure to check out Shero. They are voted by UpCity as one of the top eCommerce PPC agencies. Founded more than a decade ago, they are an eCommerce agency that is based in New York’s Hudson Valley, but also have offices in Helsinki, London, and Tirana.
Their team of almost 40 eCommerce specialists is the most skilled at helping established mid-sized to enterprise-level businesses with their Magento, Shopify Plus, or BigCommerce stores. Trusted by more than 150 brands, they have helped clients in a wide range of industries that include clothing, food and wine, as well as health, beauty, and lifestyle.
Their services include:
- Custom Shopify development and apps
- Shopify SEO
- eCommerce Growth and marketing
- Magento design and discovery
- BigCommerce project planning and discovery
22. Single Grain

Location: Los Angeles, CA
Industries: Small businesses, communications, business and finance, consumer products and services
Pricing: $10,000 minimum project size
If you need help specifically with eCommerce marketing, be sure to check out Single Grain. By using a unique digital marketing campaign for each of their clients, they have helped their clients to scale their businesses at a significant pace.
It is this customized approach that has helped them to land big clients like Airbnb, Amazon, Crunchbase, and Uber, while their happy eCommerce clients include Random House, Fujitsu and KitchenAid.
As a full-service digital agency, they also offer various other services that include:
- SEO
- PPC
- Podcast advertising
- Conversion optimization
- Content marketing
23. Evestar

Locations: Miami/Fort Lauderdale, FL; Lisbon, Portugal
Industries: Fashion and apparel, beauty and cosmetics, health and wellness, food and beverage
Pricing: Contact them for an estimate, custom pricing.
Founded only a few years ago in 2018, Evestar is one of the newer marketing agencies on our list. Their focus is to scale eCommerce D2C brands by helping them to find their “hyper-growth”. As an independent digital firm, they’re committed to delivering a personal and tailored service to all of their clients, while keeping the costs down by limiting overhead costs and commission fees.
Their holistic marketing strategies focus on social media, email marketing, and influencer marketing and they will leverage multiple of these channels to help you drive traffic.
Their specialties include:
- Email marketing
- SMS marketing
- Website design
- Video content creation
24. Storm Brain

Locations: San Diego/Los Angeles, CA; New York, NY
Industries: eCommerce, financial services, medical, retail, government
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
Storm Brain is a full-service digital brand and marketing agency that focuses on eCommerce development and services related to creative marketing.
From their offices on the East and West Coast, they implement custom strategies that take advantage of various tactics. During the 20+ years that they’ve been in business, they’ve worked with a number of well-known brands including the likes of Zillow and Century 21.
Their specialties include:
- Social media management
- Branding
- Online reputation management
- Google Ads management
25. Intero Digital (formerly SocialSEO)

Location: Colorado Springs, CO
Industries: eCommerce, retail, automotive, business and financial services, consumer products and services, hospitality and leisure, manufacturing, IT
Pricing: Project sizes often range from $10,000 to $49,000
If you are specifically searching for an agency that can help you with SEO, be sure to check out Intero Digital, known as SocialSEO before changing its name early this year. Intero Digital offers a range of eCommerce SEO strategies like conversion rate optimization and competitor research to help grow your eCommerce business.
In addition to eCommerce SEO, they also offer the following marketing services:
- Email marketing
- Amazon digital marketing
- Content strategy
- Graphic design
26. Stryde

Location: Lehi, UT
Industries: Baby and kids, fashion and apparel, home goods, sporting goods and outdoor
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
Stryde is a boutique shopper marketing agency that focuses on helping clients in the baby/mom, home, goods, fashion and apparel industries. Whether you are only starting out or have already grown your venture to a big company, their team of marketers can help you to grow your online visibility by creating and executing digital marketing strategies.
What sets them apart from most other eCommerce marketing agencies is that the majority of their team members are women. So, if you mainly target female audiences, their skills as marketers and experience as consumers can be invaluable.
Their services include:
- Technical eCommerce SEO
- Facebook and paid ads
- Email marketing
- Conversion rate optimization
27. Trellis

Locations: Boston, MA; Charleston, SC; Springfield, MO; Charlotte, NC; Denver, CO; Dubai, UAE
Industries: eCommerce, automotive, medical, manufacturing
Pricing: $150-$199 average hourly rate
Although Trellis is a full-service digital agency, they specialize in eCommerce. With the help of data-driven strategies, they drive traffic, engagement, and conversion for major B2B and B2C brands. From the automotive aftermarket to apparel and fashion, they have helped leading brands in countless different industries.
Their efforts have been recognized by BigCommerce that has included them in its list of best-in-class agencies, while UpCity has included them in their list of the top eCommerce web design agencies.
Their eCommerce services include:
- Integrations
- Marketing
- Website development
- UI/UX design
- Channel optimization
28. Upgrow

Location: San Francisco, CA
Industries: IT, business and financial services, non-profit, healthcare, B2B software, legal
Pricing: Average setup and management costs are provided on their website. Contact the agency for a more specific and comprehensive estimate.
As a digital marketing agency, Upgrow can help you with a multi-channel eCommerce marketing strategy. With the help of automation such as real-time reporting and a broken-link checker, they have more time to focus on creating an effective strategy for your brand.
They start their process with what they call hyper-targeted marketing. This way, they can help brands to identify their ideal target audience to achieve more sales and decrease ad spend.
Their full-service eCommerce marketing services include:
- SEO
- Paid search
- Social ads
- Content writing
- Conversion rate optimization
- Landing page design
29. WebFX

Locations: Harrisburg, PA (headquarters); Regional Hubs in York/Lancaster, PA; Fort Myers/Tampa, FL; Ann Arbor, MI; Cape Town, South Africa; and Guatemala. Satellite offices in 22 locations in the US.
Industries: eCommerce, business and financial services, dental, manufacturing, medical, retail, legal, energy and natural resources
Pricing: $100-$149 average hourly rate; WebFX also offers plans for specific services.
WebFX is one of the best digital marketing agencies and at the time of writing this they are the eCommerce marketing agency on Clutch with the most reviews. Founded in 2009 with locations all around the United States, their team of 200+ award-winning marketers, developers, and designers can help your eCommerce brand to create a custom strategy to meet its specific goals and needs.
Their eCommerce services include:
- Custom eCommerce SEO strategy
- eCommerce PPC
- eCommerce social media advertising
- B2B eCommerce enablement
- Walmart Marketplace advertising
- Facebook Marketplace for Business
- Shopify optimization services
- Amazon SEO and product optimization
What Are The Benefits of Hiring an eCommerce Marketing Agency?
You could have a presence on the best eCommerce platform, but if it's not supplemented with a good strategy, you'll have trouble reaching your objectives. An eCommerce marketing agency can help supplement your eCommerce presence in the following ways.
Tap into Specialized Expertise and Cutting-Edge Tools
eCommerce marketing agencies hire industry experts who know the ins and outs of all areas related to eCommerce, from social media and paid advertising to SEO and content creation.
For example, Nuanced Media has experts who have previously worked at eCommerce giants like Amazon. Similarly, Disruptive Advertising gets its up-to-date knowledge of paid search right from Google through the Google x Disruptive Summit.
These agencies are also equipped with the latest tools and technologies that might get too costly to purchase for in-house eCommerce marketing. Further, some of these agencies have their own specialized tools, such as Sellozo's Campaign Studio, that they use to manage and optimize your eCommerce campaigns.
Accelerate Success with Efficiency and Speed
Since eCommerce marketing agencies have a pre-set team of experts, they can hit the ground running as soon as you hire them. They have a streamlined process for strategy implementation based on industry best practices to give you a level of scalability you wouldn't be able to achieve if you did eCommerce marketing yourself. As your eCommerce needs grow, the agency can scale accordingly.
Gain Fresh Perspectives and Strategic Insights
Your internal team's perspective of your business is only limited to what they know. eCommerce marketing agencies have worked with numerous clients from different industries and can draw insights from those experiences to offer fresh perspectives on your business and suggest strategies that you may not have considered before.
All their strategies are data-backed for maximum results. So, it's not just a fresh perspective but also one that has proven success.
Maximize Your Budget with Cost-Effective Solutions
One thing that all eCommerce marketing agencies will tell you is that they do their best to minimize ad waste. It's a standard they hold themselves to because they want the maximum ROI for their clients.
Their PPC management services come with optimization based on A/B testing and continuous monitoring to get the best results. So, you get excellent results with a minimal budget.
For example, in a campaign for an Amazon eCommerce business, Thrive Internet Marketing Agency was able to bring a 320% increase in sales volume for them. There was also a 451% increase in unit sales, which is something the client would have found expensive to achieve with an internal marketing team. However, Thrive's expertise resulted in a 40% decrease in advertising cost of sale (ACOS) for the client.

Thrive case study
Top eCommerce Marketing Strategies That Drive Sales
Marketing for eCommerce businesses can be similar to conventional digital marketing, although with more explicit goals such as conversions. Some of the top eCommerce marketing strategies that drive sales are:
SEO and Amazon Marketing
Optimizing your website or eCommerce business page for search engines is an effective way to drive sales. Getting the coveted top spots on Google SERPs is critical to obtaining the best results. Studies have shown that less than 1% of users browse further than the first page of a search result, so ensuring that your SEO strategy is effective for your target keywords is vital.
In previous years, Google was the top choice of consumers searching for a product. In 2023, though, marketplaces have surpassed search engines to become the primary source for starting to search for products on the web.
Approximately 31% of product searches began on marketplaces like Amazon, while search engines and brand websites accounted for 14%. Amazon marketing services can be particularly beneficial since the eCommerce company accounts for 37.6% of the online retail market share in the US in 2023.
If you want to know more about SEO and eCommerce, make sure to read our guide.
Email Marketing
Ecommerce email marketing agencies and businesses use several strategies to attract customers. Email marketing can provide a high ROI with minimal costs when done right. The key is to personalize your emails, send them regularly to maintain the relationship, and ensure that the content is relevant and appealing to them. Offer exclusive discounts, loyalty promos, and other exciting deals.
Content Marketing
Content marketing should be at the forefront of eCommerce strategies for businesses with a website. Content is anything on your website, including product descriptions, which should detail the best features of your product as seen from the customer’s perspective. You can display positive reviews and customer feedback to help build your credibility and reputation.
Your landing pages should have a compelling copy that can draw your customers into your online store further down the marketing funnel. CTAs should capture the audience’s interest immediately. Finally, update your content regularly. Stale information is neither good for SEO nor attractive for potential customers.
Social Media Marketing
An excellent social media marketing strategy to incorporate is to combine your own content with user-generated content. Encourage your customers to post pictures of the products with a hashtag, and you can feature these posts on your website or your own account as social proof.
Brand awareness and customer engagement are the top goals for eCommerce social media marketing. According to HubSpot, many consumers discover new products via social media channels.
Some brands actively promote social selling, encouraging customers to purchase directly from social media. Still, you’ll see more businesses using Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and other platforms to reach customers, promote new products, engage with them, and even deliver prompt customer service.
Influencer Marketing
These days, influencers play a big role in eCommerce marketing. In 2024, 21% of consumers purchased a product recommended by an influencer. The same Hubspot report says that millennial consumers are more likely to follow an influencer’s recommendations than their friends or family. The industry is so vast that numerous influencer marketing agencies offer services specifically for brands and influencers.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Marketing
While it’s ideal to create a solid market organically, it takes time to build a base using SEO and organic marketing methods. PPC strategies, when used with SEO and social media, can push your sales and conversion rates upward faster than organic SEO alone. With PPC, you can target specific market segments and reach more people.
Mobile Optimization
An increasing number of consumers start their product searches on their mobile phones. Increase your sales by ensuring that your site is optimized for mobile. Mobile commerce is one of the top trends in eCommerce for this year, so you would miss out on a lot if you stick to desktop sites.
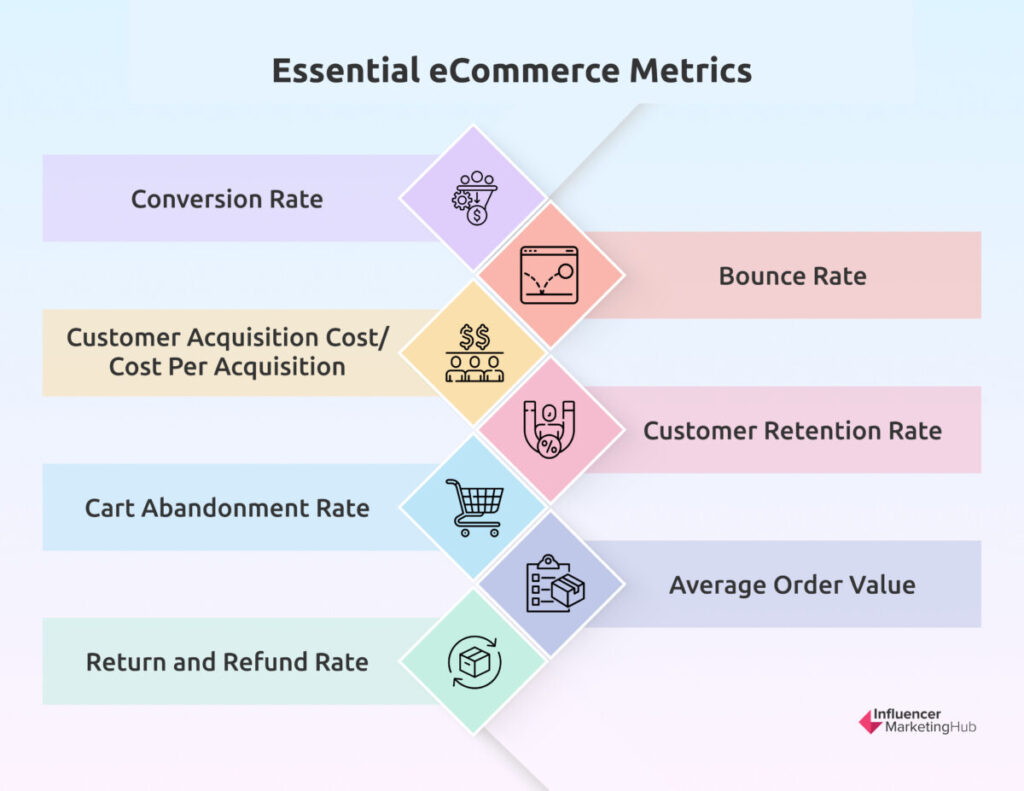
eCommerce Analytics: Measuring What Matters
Growing an eCommerce business means measuring the right key performance indicators effectively.
For instance, website traffic is an important metric to monitor, but you should go beyond counting page visits for your eCommerce business to generate profit. It’s also crucial to use these metrics to guide your decisions regarding the business; simply tracking them is only half the work. What’s important are the insights you draw from these numbers and the actions you take following those insights.
- Conversion Rate. This is the percentage of website visitors who ultimately purchase something. In 2024, the average eCommerce conversion rate hovered between 1.78% and 1.86%.
- Bounce Rate. “Bouncing” occurs when users visit a webpage and then leave almost immediately. A high bounce rate means that people leave your website without browsing or engaging and signals a need for website improvement.
- Customer Acquisition Cost/Cost Per Acquisition. This is how much it takes to acquire a customer; that is, to get someone to visit your site and complete a purchase. You calculate it by dividing your marketing expenses in a given period by the number of new customers in that same timeframe.
- Customer Retention Rate. Acquiring new customers is more costly, so many businesses also focus on retaining customers. A high customer retention rate for an eCommerce business means you have a good base of repeat customers.
- Cart Abandonment Rate. People abandon carts for many reasons, so if you see a high cart abandonment rate, it’s time to check where they tend to drop off in the checkout process so you can pinpoint the issue.
- Average Order Value. How much are people spending on your store in one order? The average order value can give you insights into your pricing and the buying patterns of your customers. You can also focus marketing efforts on customers with a high Average Order Value (AOV), ensuring they return.
- Return and Refund Rate. Returns are common in eCommerce, especially with the convenience of shipping. This can cost a business a lot, so it’s crucial to keep an eye out for this metric and draw actionable insights from it to keep your business afloat.
Utilizing AI and Machine Learning in eCommerce Marketing
AI has been a buzzword in almost all industries lately, especially with the launch of ChatGPT last year. Many consumers believe that AI will improve aspects of online shopping, such as product recommendations and price comparisons. Chatbots will likely become a permanent fixture in customer service, dealing with standard and basic customer requests quickly.
However, some consumers are still a bit skeptical about AI and would prefer human assistance in customer service.
Despite consumer hesitation over using AI for eCommerce, its benefits for marketing are substantial. Generative AI can help you write engaging product descriptions, compelling copy and CTAs for landing pages, and even personalized emails for marketing.
Some tools can even help with product research, pricing, and automation of some marketing tasks. Machine learning can be utilized to analyze a product’s sales performance so you can decide what to do next.
The usefulness of AI and machine learning is plenty; eCommerce businesses just need to know the best tools for eCommerce marketing to enhance their work. Hiring one of the top eCommerce marketing agencies listed above will also make your marketing strategy more effective by tapping into the skills and knowledge of these experts.
Add These Agencies to Your Wishlist
Even the top eCommerce companies started as small businesses. They used the resources available to them and eventually grew into successful companies that generate millions of dollars in revenue each year.
To get to that level, partnering with an eCommerce marketing agency could be a fruitful step. The agencies discussed above are masters of eCommerce marketing tools and techniques, so your business would thrive if you have one of them by your side.
They can give you the competitive edge that your business needs to stand out in the eCommerce space. More importantly, they have years of experience working with businesses like you, so they know how to handle every hurdle that comes with eCommerce marketing. Many of them offer a range of services, from SEO and email marketing to affiliate marketing and paid search. So, you can get the whole package from a single agency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Comparing the top eCommerce marketing agencies
We compared some of the best eCommerce marketing agencies, looking particularly at their past performance, industries they cater to, and the channels they excel at. Here’s our overview:
|
eCommerce Marketing Agencies |
Location | Industries | Best For | Channels |
| Sellozo | Vancouver, WA | eCommerce | Small and mid-sized businesses |
Amazon |
|
SmartSites |
Paramus, NJ | Medical and healthcare, legal, automotive, retail, B2B, hospitality, non-profit | Small and mid-sized businesses | Amazon, Google, social media |
| WEBITMD | Los Angeles, CA; Miami, FL | eCommerce, business, consumer products and services, hospitality and leisure, manufacturing | Small and mid-sized businesses |
Amazon, social media |
|
Nuanced Media |
Tucson and Phoenix, AZ | eCommerce, manufacturing, retail | Businesses of all sizes | Amazon |
| Disruptive Advertising | Pleasant Grove, UT | B2B, eCommerce, education, legal | Businesses of all sizes |
Amazon, social media |
|
Moburst |
New York, NY; San Francisco, CA; Tel Aviv, Israel; London, UK | Arts and entertainment, consumer products and services, media, supply chain and logistics, transport, utilities, eCommerce | Businesses of all sizes | Amazon, blog, Google, social media |
| Thrive Internet Marketing Agency | Various | Education and finance, health and medical, home services, manufacturing | Enterprises, large, and small brands |
Amazon, social media, Google |
Which services do the top eCommerce marketing agencies provide?
Here are some of the services provided by eCommerce marketing agencies:
|
eCommerce Marketing Agencies |
Amazon Advertising | Web Design | SEO | PPC Advertising | eCommerce Strategy Optimization |
| Sellozo | ✔ | x | x | x |
✔ |
|
SmartSites |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| WEBITMD | x | ✔ | x | ✔ |
✔ |
|
Nuanced Media |
✔ | x | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Disruptive Advertising | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
✔ |
|
Moburst |
x | x | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Thrive Internet Marketing Agency | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
✔ |
How Much Do eCommerce Marketing Agencies Cost?
The pricing for eCommerce marketing agencies differs based on their pricing model and service provision. Some agencies charge by the hour, while others charge per project. Here’s how much it costs to work with some of the best eCommerce marketing agencies.
|
eCommerce Marketing Agencies |
Pricing | Minimum Campaign Size |
| Sellozo | Flat-fee pricing; specific rates available upon request |
Upon request |
|
SmartSites |
$100-$149 average hourly rate | $1,000+ |
| WEBITMD | $150-$199 average hourly rate |
$5,000+ |
|
Nuanced Media |
$100-$149 average hourly rate | $1,000+ |
| Disruptive Advertising | $100-$149 average hourly rate |
$5,000+ |
|
Moburst |
$150-$199 average hourly rate | $5,000+ |
| Thrive Internet Marketing Agency | $100-149 average hourly rate |
$1,000+ |
What are the best eCommerce marketing agencies in USA?
Since the US is the largest contributor to the global eCommerce industry, it makes sense for the country to have a lot of competent eCommerce marketing agencies. Some of them include:
- SmartSites
- WEBITMD
- Nuanced Media
- Disruptive Advertising
- Moburst
- Thrive Internet Marketing Agency
- Sociallyin
What are the best full-service eCommerce marketing agencies?
Full-service eCommerce marketing agencies provide pretty much all services an eCommerce business could need, including SEO, email marketing, and more. Here are some of these agencies:
- Disruptive Advertising
- Moburst
- Thrive Internet Marketing Agency
- Absolute Web
- DigitlHaus
- Groove
What are the top eCommerce agencies for web design?
Many eCommerce agencies web design services to create a client’s online presence from scratch. Some eCommerce agencies for web design are:
- SmartSites
- WEBITMD
- Thrive internet Marketing Agency
- Ninja Promo
- Trellis
What are the top eCommerce SEO agencies?
The following eCommerce agencies offer SEO as one of their services:
- SmartSites
- Thrive internet Marketing Agency
- Sociallyin
- 1Digital Agency
- Intero Digital
- WebFX
Is it better to hire a full-service eCommerce agency or a specialized one?
It depends on your needs. Full-service agencies offer a wide range of services under one roof, which can be convenient for businesses looking for a comprehensive marketing solution. Specialized agencies focus on a particular aspect of marketing (e.g., SEO), making them a better choice if you need deep expertise in one area.
Should I hire a digital marketing agency for my small e-commerce business?
If you're making a net profit of around $5 and you don't mind investing back into the business, you can work with an eCommerce marketing agency to scale your business. Initially, it may seem like an added cost, but in the long run, it can bring in a significant return on investment.